Thyrocyte-specific inactivation of p53 and Pten results in anaplastic thyroid carcinomas faithfully recapitulating human tumors
- PMID: 22190384
- PMCID: PMC3282070
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.380
Thyrocyte-specific inactivation of p53 and Pten results in anaplastic thyroid carcinomas faithfully recapitulating human tumors
Abstract
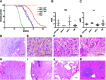
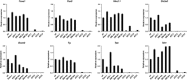
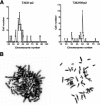
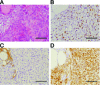
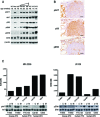
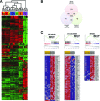
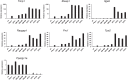
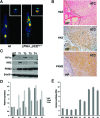
Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma (ATC) is the most aggressive form of thyroid cancer, and often derives from pre-existing well-differentiated tumors. Despite a relatively low prevalence, it accounts for a disproportionate number of thyroid cancer-related deaths, due to its resistance to any therapeutic approach. Here we describe the first mouse model of ATC, obtained by combining in the mouse thyroid follicular cells two molecular hallmarks of human ATC: activation of PI3K (via Pten deletion) and inactivation of p53. By 9 months of age, over 75% of the compound mutant mice develop aggressive, undifferentiated thyroid tumors that evolve from pre-existing follicular hyperplasia and carcinoma. These tumors display all the features of their human counterpart, including pleomorphism, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, aneuploidy, local invasion, and distant metastases. Expression profiling of the murine ATCs reveals a significant overlap with genes found deregulated in human ATC, including genes involved in mitosis control. Furthermore, similar to the human tumors, [Pten, p53]thyr-/- tumors and cells are highly glycolytic and remarkably sensitive to glycolysis inhibitors, which synergize with standard chemotherapy. Taken together, our results show that combined PI3K activation and p53 loss faithfully reproduce the development of thyroid anaplastic carcinomas, and provide a compelling rationale for targeting glycolysis to increase chemotherapy response in ATC patients.
Figures
References
-
- Burns WR, Zeiger MA. Differentiated thyroid cancer. Semin Oncol. 2010;37:557–566. - PubMed
-
- Wang HM, Huang YW, Huang JS, Wang CH, Kok VC, Hung CM, Chen HM, Tzen CY. Anaplastic carcinoma of the thyroid arising more often from follicular carcinoma than papillary carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14:3011–3018. - PubMed
-
- Quiros RM, Ding HG, Gattuso P, Prinz RA, Xu X. Evidence that one subset of anaplastic thyroid carcinomas are derived from papillary carcinomas due to BRAF and p53 mutations. Cancer. 2005;103:2261–2268. - PubMed
-
- Cornett WR, Sharma AK, Day TA, Richardson MS, Hoda RS, van Heerden JA, Fernandes JK. Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: an overview. Curr Oncol Rep. 2007;9:152–158. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

