The transcriptional coactivator TAZ regulates mesenchymal differentiation in malignant glioma
- PMID: 22190458
- PMCID: PMC3248681
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.176800.111
The transcriptional coactivator TAZ regulates mesenchymal differentiation in malignant glioma
Abstract
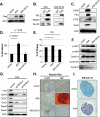
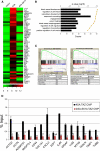
Recent molecular classification of glioblastoma (GBM) has shown that patients with a mesenchymal (MES) gene expression signature exhibit poor overall survival and treatment resistance. Using regulatory network analysis of available expression microarray data sets of GBM, including The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), we identified the transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif (TAZ), to be highly associated with the MES network. TAZ expression was lower in proneural (PN) GBMs and lower-grade gliomas, which correlated with CpG island hypermethylation of the TAZ promoter compared with MES GBMs. Silencing of TAZ in MES glioma stem cells (GSCs) decreased expression of MES markers, invasion, self-renewal, and tumor formation. Conversely, overexpression of TAZ in PN GSCs as well as murine neural stem cells (NSCs) induced MES marker expression and aberrant osteoblastic and chondrocytic differentiation in a TEAD-dependent fashion. Using chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), we show that TAZ is directly recruited to a majority of MES gene promoters in a complex with TEAD2. The coexpression of TAZ, but not a mutated form of TAZ that lacks TEAD binding, with platelet-derived growth factor-B (PDGF-B) resulted in high-grade tumors with MES features in a murine model of glioma. Our studies uncover a direct role for TAZ and TEAD in driving the MES differentiation of malignant glioma.
© 2011 by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press
Figures




Comment in
-
Cancer stem cells: TAZ takes centre stage.Nat Rev Cancer. 2012 Jan 19;12(2):82-3. doi: 10.1038/nrc3210. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22257952 No abstract available.
References
-
- Anido J, Saez-Borderias A, Gonzalez-Junca A, Rodon L, Folch G, Carmona MA, Prieto-Sanchez RM, Barba I, Martinez-Saez E, Prudkin L, et al. 2010. TGF-β receptor inhibitors target the CD44(high)/Id1(high) glioma-initiating cell population in human glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 18: 655–668 - PubMed
-
- Bachoo RM, Maher EA, Ligon KL, Sharpless NE, Chan SS, You MJ, Tang Y, DeFrances J, Stover E, Weissleder R, et al. 2002. Epidermal growth factor receptor and Ink4a/Arf: Convergent mechanisms governing terminal differentiation and transformation along the neural stem cell to astrocyte axis. Cancer Cell 1: 269–277 - PubMed
-
- Basu S, Totty NF, Irwin MS, Sudol M, Downward J 2003. Akt phosphorylates the Yes-associated protein, YAP, to induce interaction with 14-3-3 and attenuation of p73-mediated apoptosis. Mol Cell 11: 11–23 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
