In vivo analysis of compound activity and mechanism of action using epistasis in Drosophila
- PMID: 22190992
- PMCID: PMC3077214
- DOI: 10.1007/s12154-010-0051-5
In vivo analysis of compound activity and mechanism of action using epistasis in Drosophila
Abstract
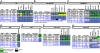
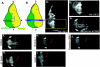
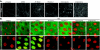
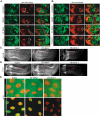
The recent establishment of high-throughput methods for culturing Drosophila provided a unique ability to screen compound libraries against complex disease phenotypes in the context of whole animals. However, as compound studies in Drosophila have been limited so far, the degree of conservation of compound activity between Drosophila and vertebrates or the effectiveness of feeding as a compound delivery system is not well known. Our comprehensive in vivo analysis of 27 small molecules targeting seven signaling pathways in Drosophila revealed a high degree of conservation of compound activity between Drosophila and vertebrates. We also investigated the mechanism of action of AY9944, one of the Hh pathway antagonists that we identified in our compound feeding experiments. Our epistasis analysis of AY9944 provided novel insights into AY9944's mechanism of action and revealed a novel role for cholesterol transport in Hh signal transduction.
Electronic supplementary material: The online version of this article (doi:10.1007/s12154-010-0051-5) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Chemical genetics; Compound feeding; Drosophila; Drug discovery; Signal transduction.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Simplification traps.J Chem Biol. 2012 Jan;5(1):1-4. doi: 10.1007/s12154-011-0069-3. Epub 2011 Dec 7. J Chem Biol. 2012. PMID: 23226811 Free PMC article.
-
In-cell click labelling of small molecules to determine subcellular localisation.J Chem Biol. 2011 Apr;4(2):49-53. doi: 10.1007/s12154-010-0047-1. Epub 2010 Nov 18. J Chem Biol. 2011. PMID: 22096474 Free PMC article.
-
A Drosophila Based Cancer Drug Discovery Framework.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1167:237-248. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-23629-8_14. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31520359 Review.
-
Hedgehog and its patched-smoothened receptor complex: a novel signalling mechanism at the cell surface.Biol Chem. 1997 Jul;378(7):583-90. doi: 10.1515/bchm.1997.378.7.583. Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9278137 Review.
-
Emerging roles for hedgehog-patched-Gli signal transduction in reproduction.Biol Reprod. 2003 Jul;69(1):8-14. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.103.015941. Epub 2003 Apr 2. Biol Reprod. 2003. PMID: 12672657 Review.
Cited by
-
ERK signaling couples nutrient status to antiviral defense in the insect gut.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Sep 10;110(37):15025-30. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1303193110. Epub 2013 Aug 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23980175 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term in vivo imaging of Drosophila larvae.Nat Protoc. 2020 Mar;15(3):1158-1187. doi: 10.1038/s41596-019-0282-z. Epub 2020 Feb 10. Nat Protoc. 2020. PMID: 32042177
-
Immune response to bacteria induces dissemination of Ras-activated Drosophila hindgut cells.EMBO Rep. 2012 Jun 1;13(6):569-76. doi: 10.1038/embor.2012.44. EMBO Rep. 2012. PMID: 22498775 Free PMC article.
-
A Personalized Therapeutics Approach Using an In Silico Drosophila Patient Model Reveals Optimal Chemo- and Targeted Therapy Combinations for Colorectal Cancer.Front Oncol. 2021 Jul 16;11:692592. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.692592. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34336681 Free PMC article.
-
A Drosophila chemical screen reveals synergistic effect of MEK and DGKα inhibition in Ras-driven cancer.Dis Model Mech. 2023 Mar 1;16(3):dmm049769. doi: 10.1242/dmm.049769. Epub 2023 Apr 3. Dis Model Mech. 2023. PMID: 36861754 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baxter ADA, Boyd Edward Andrew, Guicherit Oivin M, Price Stephen, Rubin Lee D (2003) Mediators of hedgehog signaling pathways, compositions and uses related thereto. Curtis, Inc., Cambridge, MA
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

