Imatinib Mesylate for Patients with Recurrent or Metastatic Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors Expressing KIT: A Decade Experience from Taiwan
- PMID: 22190996
- PMCID: PMC3243655
- DOI: 10.1593/tlo.11253
Imatinib Mesylate for Patients with Recurrent or Metastatic Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors Expressing KIT: A Decade Experience from Taiwan
Abstract
Purpose: Our preliminary report of imatinib mesylate (IM) in gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) patients detailed a high response rate; however, the long-term result is still unknown. We conducted an analysis of Taiwan advanced inoperable/metastatic GIST patients treated on IM regarding survival, pattern of failure, potential prognostic factors, and mutational status.
Patients and methods: From 2001 to 2010, patients with pathologically proven advanced inoperable/metastatic GIST receiving IM were enrolled onto this study. Data on KIT mutational status, measurable tumor size, and other potential prognostic factors were prospectively collected. Patients were followed up for a median of 33.6 months.
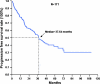
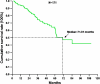
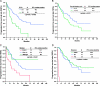
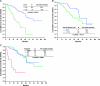
Results: There were 171 patients (106 men and 65 women) with response rate, and their clinical benefit for IM was 57.3% and 87.1%, respectively. Median progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) for these 171 patients are 37.6 and 71.0 months, respectively. Of 171 patients, 120 (70.2%) remained on long-term IM use. Poor performance status, tumor larger than 11.5 cm, primary resistance, and the presence of an exon 9 mutation were independently associated with unfavorable PFS. Regarding OS, poor performance status, primary resistance, and tumor larger than 11.5 cm were three independently unfavorable predictors.
Conclusions: The median PFS and OS of 171 GIST patients are 37.6 and 71.0 months, respectively. Poor performance status, tumor size larger than 11.5 cm, primary resistance, and an exon 9 mutation were independently associated with unfavorable PFS. Regarding OS, poor performance status, primary resistance, and tumor size larger than 11.5 cm were three independent unfavorable predictors.
Figures
References
-
- Blanke CD, Corless CL. State-of-the art therapy for gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Cancer Invest. 2005;23:274–280. - PubMed
-
- Hirota S, Isozaki K, Moriyama Y, Hashimoto K, Nishida T, Ishiguro S, Kawano K, Hanada M, Kurata A, Takeda M, et al. Gain-of-function mutations of c-kit in human gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science. 1998;279:577–580. - PubMed
-
- Druker BJ, Tamura S, Buchdunger E, Ohno S, Segal GM, Fanning S, Zimmermann J, Lydon NB. Effects of a selective inhibitor of the Abl tyrosine kinase on the growth of Bcr-Abl positive cells. Nat Med. 1996;2:561–566. - PubMed
-
- Buchdunger E, Cioffi CL, Law N, Stover D, Ohno-Jones S, Druker BJ, Lydon NB. Abl protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitor STI571 inhibits in vitro signal transduction mediated by c-kit and platelet-derived growth factor receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000;295:139–145. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
