P-glycoprotein silencing with siRNA delivered by DOPE-modified PEI overcomes doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer cells
- PMID: 22191778
- PMCID: PMC3422569
- DOI: 10.2217/nnm.11.93
P-glycoprotein silencing with siRNA delivered by DOPE-modified PEI overcomes doxorubicin resistance in breast cancer cells
Abstract
Aims: Multidrug resistance (MDR) mediated by overexpression of drug efflux transporters such as P-glycoprotein (P-gp), is a major problem, limiting successful chemotherapy of breast cancer. The use of siRNA to inhibit P-gp expression in MDR tumors is an attractive strategy to improve the effectiveness of anticancer drugs.
Method: We have synthesized a novel conjugate between a phospholipid (dioleoylphosphatidylethanolamine) and polyethylenimine (PEI) for siRNA delivery, for the purpose of silencing P-gp to overcome doxorubicin resistance in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells.
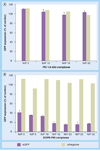
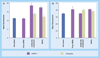
Results: The dioleoylphosphatidylethanolamine-PEI conjugate enhanced the transfection efficacy of low-molecular-weight PEI, which was otherwise totally ineffective. In addition, the polyethylene glycol/lipid coating of the new complexes gave rise to small micelle-like nanoparticles with improved biocompatibility properties. Both coated and noncoated formulations delivered P-gp-specific siRNA to MDR cells.
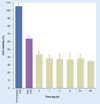
Discussion: The combination of doxorubicin and P-gp silencing formulations led to a twofold increase of doxorubicin uptake and a significant improvement of the therapeutic effect of doxorubicin in resistant cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures




References
-
- Gillet JP, Gottesman MM. Mechanisms of multidrug resistance in cancer. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010;596:47–76. - PubMed
-
- Constantinides PP, Wasan KM. Lipid formulation strategies for enhancing intestinal transport and absorption of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) substrate drugs: in vitro/in vivo case studies. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007;96:235–248. - PubMed
-
-
Staud F, Ceckova M, Micuda S, Pavek P. Expression and function of p-glycoprotein in normal tissues: effect on pharmacokinetics. Methods Mol. Biol. 2010;596:199–222. ▪ A comprehensive review of the physiological role of P-glycoprotein in normal tissues and its impact on the final fate of drugs.
-
-
- Marzolini C, Paus E, Buclin T, Kim RB. Polymorphisms in human MDR1 (P-glycoprotein): recent advances and clinical relevance. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004;75:13–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
