Morphine metabolism, transport and brain disposition
- PMID: 22193538
- PMCID: PMC3276770
- DOI: 10.1007/s11011-011-9274-6
Morphine metabolism, transport and brain disposition
Abstract
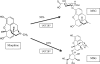
The chemical structures of morphine and its metabolites are closely related to the clinical effects of drugs (analgesia and side-effects) and to their capability to cross the Blood Brain Barrier (BBB). Morphine-6-glucuronide (M6G) and Morphine-3-glucuronide (M3G) are both highly hydrophilic, but only M6G can penetrate the BBB; accordingly, M6G is considered a more attractive analgesic than the parent drug and the M3G. Several hypotheses have been made to explain these differences. In this review we will discuss recent advances in the field, considering brain disposition of M6G, UDP-glucoronosyltransferases (UGT) involved in morphine metabolism, UGT interindividual variability and transport proteins.
Figures
References
-
- Allegri M, De Gregori M, Niebel T, et al. Pharmacogenetics and postoperative pain: a new approach to improve acute pain management. Minerva Anestesiol. 2010;76(11):937–44. - PubMed
-
- Bouw MR, Tunblad K, Hammarlund-Udenaes M. Blood Brain Barrier transport and brain distribution of morphine-6-glucuronide in relation to the antinociceptive effect in rats – pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modelling. Br J Pharmacol. 2001;134:1796–1804. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704406. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources