Redox signalling directly regulates TDP-43 via cysteine oxidation and disulphide cross-linking
- PMID: 22193716
- PMCID: PMC3297986
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2011.471
Redox signalling directly regulates TDP-43 via cysteine oxidation and disulphide cross-linking
Abstract
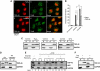
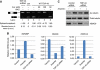
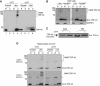
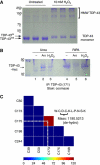
TDP-43 is the major disease protein in ubiquitin-positive inclusions of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) characterized by TDP-43 pathology (FTLD-TDP). Accumulation of insoluble TDP-43 aggregates could impair normal TDP-43 functions and initiate disease progression. Thus, it is critical to define the signalling mechanisms regulating TDP-43 since this could open up new avenues for therapeutic interventions. Here, we have identified a redox-mediated signalling mechanism directly regulating TDP-43. Using in vitro and cell-based studies, we demonstrate that oxidative stress promotes TDP-43 cross-linking via cysteine oxidation and disulphide bond formation leading to decreased TDP-43 solubility. Biochemical analysis identified several cysteine residues located within and adjacent to the second RNA-recognition motif that contribute to both intra- and inter-molecular interactions, supporting TDP-43 as a target of redox signalling. Moreover, increased levels of cross-linked TDP-43 species are found in FTLD-TDP brains, indicating that aberrant TDP-43 cross-linking is a prominent pathological feature of this disease. Thus, TDP-43 is dynamically regulated by a redox regulatory switch that links oxidative stress to the modulation of TDP-43 and its downstream targets.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Agar J, Durham H (2003) Relevance of oxidative injury in the pathogenesis of motor neuron diseases. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 4: 232–242 - PubMed
-
- Ayala YM, Pantano S, D'Ambrogio A, Buratti E, Brindisi A, Marchetti C, Romano M, Baralle FE (2005) Human Drosophila and C. elegans TDP43: nucleic acid binding properties and splicing regulatory function. J Mol Biol 348: 575–588 - PubMed
-
- Ayala YM, Zago P, D'Ambrogio A, Xu YF, Petrucelli L, Buratti E, Baralle FE (2008) Structural determinants of the cellular localization and shuttling of TDP-43. J Cell Sci 121: 3778–3785 - PubMed
-
- Benoit RM, Meisner NC, Kallen J, Graff P, Hemmig R, Cèbe R, Ostermeier C, Widmer H, Auer M (2010) The x-ray crystal structure of the first RNA recognition motif and site-directed mutagenesis suggest a possible HuR redox sensing mechanism. J Mol Biol 397: 1231–1244 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

