Mechanism of nucleotide sensing in group II chaperonins
- PMID: 22193720
- PMCID: PMC3273386
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2011.468
Mechanism of nucleotide sensing in group II chaperonins
Erratum in
- EMBO J. 2012 Oct 3;31(19):3949-50
Abstract
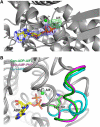
Group II chaperonins mediate protein folding in an ATP-dependent manner in eukaryotes and archaea. The binding of ATP and subsequent hydrolysis promotes the closure of the multi-subunit rings where protein folding occurs. The mechanism by which local changes in the nucleotide-binding site are communicated between individual subunits is unknown. The crystal structure of the archaeal chaperonin from Methanococcus maripaludis in several nucleotides bound states reveals the local conformational changes associated with ATP hydrolysis. Residue Lys-161, which is extremely conserved among group II chaperonins, forms interactions with the γ-phosphate of ATP but shows a different orientation in the presence of ADP. The loss of the ATP γ-phosphate interaction with Lys-161 in the ADP state promotes a significant rearrangement of a loop consisting of residues 160-169. We propose that Lys-161 functions as an ATP sensor and that 160-169 constitutes a nucleotide-sensing loop (NSL) that monitors the presence of the γ-phosphate. Functional analysis using NSL mutants shows a significant decrease in ATPase activity, suggesting that the NSL is involved in timing of the protein folding cycle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
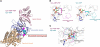

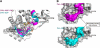


References
-
- Adams PD, Afonine PV, Bunkóczi G, Chen VB, Davis IW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Hung LW, Kapral GJ, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, McCoy AJ, Moriarty NW, Oeffner R, Read RJ, Richardson DC, Richardson JS, Terwilliger TC, Zwart PH (2010) PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallogr D 66: 213–221 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bigotti MG, Bellamy SR, Clarke AR (2006) The asymmetric ATPase cycle of the Thermosome: elucidation of the binding, hydrolysis and product-release steps. J Mol Biol 362: 835–843 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

