Competition between sumoylation and ubiquitination of serine hydroxymethyltransferase 1 determines its nuclear localization and its accumulation in the nucleus
- PMID: 22194612
- PMCID: PMC3281627
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.302174
Competition between sumoylation and ubiquitination of serine hydroxymethyltransferase 1 determines its nuclear localization and its accumulation in the nucleus
Abstract
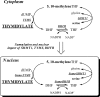
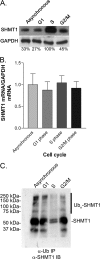
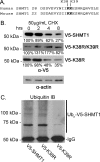
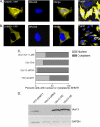
Serine hydroxymethyltransferase 1 (SHMT1) expression limits rates of de novo dTMP synthesis in the nucleus. Here we report that SHMT1 is ubiquitinated at the small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) consensus motif and that ubiquitination at that site is required for SHMT1 degradation. SHMT1 protein levels are cell cycle-regulated, and Ub-SHMT1 levels are lowest at S phase when SHMT1 undergoes SUMO modification and nuclear transport. Mutation of the SUMO consensus motif increases SHMT1 stability. SHMT1 interacts with components of the proteasome in both the nucleus and cytoplasm, indicating that degradation occurs in both compartments. Ubc13-mediated ubiquitination is required for SHMT1 nuclear export and increases stability of SHMT1 within the nucleus, whereas Ubc9-mediated modification with Sumo2/3 is involved in nuclear degradation. These data demonstrate that SUMO and ubiquitin modification of SHMT1 occurs on the same lysine residue and determine the localization and accumulation of SHMT1 in the nucleus.
Figures







References
-
- Deleted in proof
-
- Woeller C. F., Anderson D. D., Szebenyi D. M., Stover P. J. (2007) Evidence for small ubiquitin-like modifier-dependent nuclear import of the thymidylate biosynthesis pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 17623–17631 - PubMed
-
- Anderson D. D., Woeller C. F., Stover P. J. (2007) Small ubiquitin-like modifier-1 (SUMO-1) modification of thymidylate synthase and dihydrofolate reductase. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 45, 1760–1763 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

