Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect: does age matter?
- PMID: 22194756
- PMCID: PMC3242016
- DOI: 10.4070/kcj.2011.41.11.633
Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect: does age matter?
Abstract
Atrial septal defect (ASD) is the most common type of common congenital heart disease (CHD) in adults. During the last decade, there has been a remarkable change in the treatment strategy of ASD, shifting the therapeutic gold standard from surgery to transcatheter closure, along with refinements and the evolution of device technology. Reports on the outcome of transcatheter ASD closure have shown an excellent efficacy as well as a low complication rate. However, the procedural details and/or outcomes of this procedure may be influenced by several factors including morphologic characteristics of the defect, co-morbid diseases, as well as individual factors including age and weight of the patient. Because the risk-benefit relationship in both the very young and the elderly subsets of the patients has not been clearly defined yet, closure of an ASD with device may be potentially subtracted from the treatment option in these patient groups. In this article, we will review the basis for device closure in small children and elderly patients with ASD and provide an overview of the frequently encountered problems.
Keywords: Aged; Atrial septal defect; Child; Septal occluder device.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
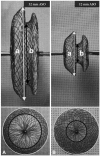

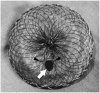
References
-
- Park MK. Pediatric Cardiology for Practitioners. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Mosby Elsevier; 2008. pp. 161–191.
-
- Lammers A, Hager A, Eicken A, Lange R, Hauser M, Hess J. Need for closure of secundum atrial septal defect in infancy. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2005;129:1353–1357. - PubMed
-
- Hijazi ZM, Celiker A. Closure of atrial septal defects. Anadolu Kardiyol Derg. 2005;5:331. - PubMed
-
- Holzer R, Hijazi ZM. Interventional approach to congenital heart disease. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2004;19:84–90. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

