In silico analysis of conformational changes induced by mutation of aromatic binding residues: consequences for drug binding in the hERG K+ channel
- PMID: 22194911
- PMCID: PMC3240635
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028778
In silico analysis of conformational changes induced by mutation of aromatic binding residues: consequences for drug binding in the hERG K+ channel
Abstract
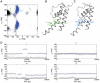
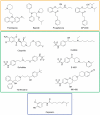
Pharmacological inhibition of cardiac hERG K(+) channels is associated with increased risk of lethal arrhythmias. Many drugs reduce hERG current by directly binding to the channel, thereby blocking ion conduction. Mutation of two aromatic residues (F656 and Y652) substantially decreases the potency of numerous structurally diverse compounds. Nevertheless, some drugs are only weakly affected by mutation Y652A. In this study we utilize molecular dynamics simulations and docking studies to analyze the different effects of mutation Y652A on a selected number of hERG blockers. MD simulations reveal conformational changes in the binding site induced by mutation Y652A. Loss of π-π-stacking between the two aromatic residues induces a conformational change of the F656 side chain from a cavity facing to cavity lining orientation. Docking studies and MD simulations qualitatively reproduce the diverse experimentally observed modulatory effects of mutation Y652A and provide a new structural interpretation for the sensitivity differences.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
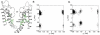



References
-
- Sanguinetti MC, Jiang C, Curran ME, Keating MT. A mechanistic link between an inherited and an acquired cardiac arrhythmia: HERG encodes the IKr potassium channel. Cell. 1995;81:299–307. - PubMed
-
- Jurkiewicz NK, Sanguinetti MC. Rate-dependent prolongation of cardiac action potentials by a methanesulfonanilide class III antiarrhythmic agent. Specific block of rapidly activating delayed rectifier K+ current by dofetilide. Circ Res. 1993;72:75–83. - PubMed
-
- Tseng GN. I(Kr): the hERG channel. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2001;33:835–849. - PubMed
-
- Haverkamp W, Breithardt G, Camm AJ, Janse MJ, Rosen MR, et al. The potential for QT prolongation and proarrhythmia by non-antiarrhythmic drugs: clinical and regulatory implications. Report on a policy conference of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur Heart J. 2000;21:1216–1231. - PubMed
-
- Vandenberg J, Walker B, Campbell T. HERG K+ channels: friend and foe. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2001;22:240–246. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

