Additive antinociceptive effects of a combination of vitamin C and vitamin E after peripheral nerve injury
- PMID: 22195029
- PMCID: PMC3237606
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029240
Additive antinociceptive effects of a combination of vitamin C and vitamin E after peripheral nerve injury
Abstract
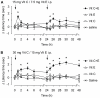
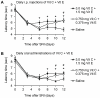
Accumulating evidence indicates that increased generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) contributes to the development of exaggerated pain hypersensitivity during persistent pain. In the present study, we investigated the antinociceptive efficacy of the antioxidants vitamin C and vitamin E in mouse models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. We show that systemic administration of a combination of vitamins C and E inhibited the early behavioral responses to formalin injection and the neuropathic pain behavior after peripheral nerve injury, but not the inflammatory pain behavior induced by Complete Freund's Adjuvant. In contrast, vitamin C or vitamin E given alone failed to affect the nociceptive behavior in all tested models. The attenuated neuropathic pain behavior induced by the vitamin C and E combination was paralleled by a reduced p38 phosphorylation in the spinal cord and in dorsal root ganglia, and was also observed after intrathecal injection of the vitamins. Moreover, the vitamin C and E combination ameliorated the allodynia induced by an intrathecally delivered ROS donor. Our results suggest that administration of vitamins C and E in combination may exert synergistic antinociceptive effects, and further indicate that ROS essentially contribute to nociceptive processing in special pain states.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
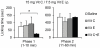
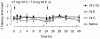
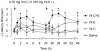


Similar articles
-
Upregulation of neuregulin-1 reverses signs of neuropathic pain in rats.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Aug 15;7(9):5916-21. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25337235 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of spinal MAPKs by scorpion venom peptide BmK AGAP produces a sensory-specific analgesic effect.Mol Pain. 2018 Jan-Dec;14:1744806918761238. doi: 10.1177/1744806918761238. Epub 2018 Feb 9. Mol Pain. 2018. PMID: 29424271 Free PMC article.
-
Up-regulation of platelet-activating factor synthases and its receptor in spinal cord contribute to development of neuropathic pain following peripheral nerve injury.Mol Pain. 2012 Feb 2;8:8. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-8-8. Mol Pain. 2012. PMID: 22296727 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal astrocytic c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) activation as counteracting mechanism to the amitriptyline analgesic efficacy in painful peripheral neuropathies.Eur J Pharmacol. 2017 Mar 5;798:85-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.01.025. Epub 2017 Jan 21. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28119076
-
SIRT1: A promising therapeutic target for chronic pain.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022 Jun;28(6):818-828. doi: 10.1111/cns.13838. Epub 2022 Apr 9. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2022. PMID: 35396903 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanism-based treatment for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathic pain.Nat Rev Neurol. 2014 Dec;10(12):694-707. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2014.211. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Nat Rev Neurol. 2014. PMID: 25366108 Review.
-
Ascorbic Acid interaction with analgesic effect of morphine and tramadol in mice.Anesth Pain Med. 2014 Jun 22;4(3):e19529. doi: 10.5812/aapm.19529. eCollection 2014 Aug. Anesth Pain Med. 2014. PMID: 25289375 Free PMC article.
-
Selection of sciatic nerve injury models: implications for pathogenesis and treatment.Front Neurol. 2025 May 7;16:1521941. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1521941. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40401028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of NOX2 signaling limits pain-related behavior and improves motor function in male mice after spinal cord injury: Participation of IL-10/miR-155 pathways.Brain Behav Immun. 2019 Aug;80:73-87. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2019.02.024. Epub 2019 Feb 23. Brain Behav Immun. 2019. PMID: 30807841 Free PMC article.
-
Ascorbic Acid Facilitates Neural Regeneration After Sciatic Nerve Crush Injury.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Mar 21;13:108. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00108. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30949031 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lau AT, Wang Y, Chiu JF. Reactive oxygen species: current knowledge and applications in cancer research and therapeutic. J Cell Biochem. 2008;104:657–667. - PubMed
-
- Sorce S, Krause KH. NOX enzymes in the central nervous system: from signaling to disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2009;11:2481–2504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

