Additive antinociceptive effects of a combination of vitamin C and vitamin E after peripheral nerve injury
- PMID: 22195029
- PMCID: PMC3237606
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029240
Additive antinociceptive effects of a combination of vitamin C and vitamin E after peripheral nerve injury
Abstract
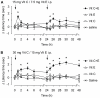
Accumulating evidence indicates that increased generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) contributes to the development of exaggerated pain hypersensitivity during persistent pain. In the present study, we investigated the antinociceptive efficacy of the antioxidants vitamin C and vitamin E in mouse models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. We show that systemic administration of a combination of vitamins C and E inhibited the early behavioral responses to formalin injection and the neuropathic pain behavior after peripheral nerve injury, but not the inflammatory pain behavior induced by Complete Freund's Adjuvant. In contrast, vitamin C or vitamin E given alone failed to affect the nociceptive behavior in all tested models. The attenuated neuropathic pain behavior induced by the vitamin C and E combination was paralleled by a reduced p38 phosphorylation in the spinal cord and in dorsal root ganglia, and was also observed after intrathecal injection of the vitamins. Moreover, the vitamin C and E combination ameliorated the allodynia induced by an intrathecally delivered ROS donor. Our results suggest that administration of vitamins C and E in combination may exert synergistic antinociceptive effects, and further indicate that ROS essentially contribute to nociceptive processing in special pain states.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
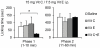
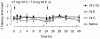
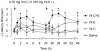
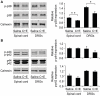

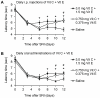

References
-
- Lau AT, Wang Y, Chiu JF. Reactive oxygen species: current knowledge and applications in cancer research and therapeutic. J Cell Biochem. 2008;104:657–667. - PubMed
-
- Sorce S, Krause KH. NOX enzymes in the central nervous system: from signaling to disease. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2009;11:2481–2504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

