Synchrotron radiation X-ray microfluorescence reveals polarized distribution of atomic elements during differentiation of pluripotent stem cells
- PMID: 22195032
- PMCID: PMC3241705
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029244
Synchrotron radiation X-ray microfluorescence reveals polarized distribution of atomic elements during differentiation of pluripotent stem cells
Abstract
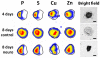
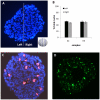
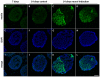
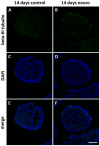
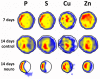
The mechanisms underlying pluripotency and differentiation in embryonic and reprogrammed stem cells are unclear. In this work, we characterized the pluripotent state towards neural differentiated state through analysis of trace elements distribution using the Synchrotron Radiation X-ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy. Naive and neural-stimulated embryoid bodies (EB) derived from embryonic and induced pluripotent stem (ES and iPS) cells were irradiated with a spatial resolution of 20 µm to make elemental maps and qualitative chemical analyses. Results show that these embryo-like aggregates exhibit self-organization at the atomic level. Metallic elements content rises and consistent elemental polarization pattern of P and S in both mouse and human pluripotent stem cells were observed, indicating that neural differentiation and elemental polarization are strongly correlated.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


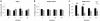
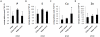

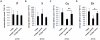

References
-
- Smith A. The battlefield of pluripotency. Cell. 2005;123:757–760. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126:663–676. - PubMed
-
- Chan EM, Ratanasirintrawoot S, Park IH, Manos PD, Loh YH, et al. Live cell imaging distinguishes bona fide human iPS cells from partially reprogrammed cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2009;27:1033–1037. - PubMed
-
- Qin J, Guo X, Cui GH, Zhou YC, Zhou DR, et al. Cluster characterization of mouse embryonic stem cell-derived pluripotent embryoid bodies in four distinct developmental stages. Biologicals. 2009;37:235–244. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

