Circulating and brain BDNF levels in stroke rats. Relevance to clinical studies
- PMID: 22195050
- PMCID: PMC3241711
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029405
Circulating and brain BDNF levels in stroke rats. Relevance to clinical studies
Abstract
Background: Whereas brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels are measured in the brain in animal models of stroke, neurotrophin levels in stroke patients are measured in plasma or serum samples. The present study was designed to investigate the meaning of circulating BDNF levels in stroke patients.
Methods and results: Unilateral ischemic stroke was induced in rats by the injection of various numbers of microspheres into the carotid circulation in order to mimic the different degrees of stroke severity observed in stroke patients. Blood was serially collected from the jugular vein before and after (4 h, 24 h and 8 d) embolization and the whole brains were collected at 4, 24 h and 8 d post-embolization. Rats were then selected from their degree of embolization, so that the distribution of stroke severity in the rats at the different time points was large but similar. Using ELISA tests, BDNF levels were measured in plasma, serum and brain of selected rats. Whereas plasma and serum BDNF levels were not changed by stroke, stroke induced an increase in brain BDNF levels at 4 h and 24 h post-embolization, which was not correlated with stroke severity. Individual plasma BDNF levels did not correlate with brain levels at any time point after stroke but a positive correlation (r = 0.67) was observed between individual plasma BDNF levels and stroke severity at 4 h post-embolization.
Conclusion: Circulating BDNF levels do not mirror brain BDNF levels after stroke, and severe stroke is associated with high plasma BDNF in the very acute stage.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
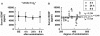



Similar articles
-
Elevated brain derived neurotrophic factor levels in plasma reflect in vivo functional viability of infused mesenchymal stem cells for stroke in rats.J Neurosurg Sci. 2019 Feb;63(1):42-49. doi: 10.23736/S0390-5616.17.03989-3. Epub 2017 Feb 8. J Neurosurg Sci. 2019. PMID: 28181779
-
Relevance of Post-Stroke Circulating BDNF Levels as a Prognostic Biomarker of Stroke Outcome. Impact of rt-PA Treatment.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 15;10(10):e0140668. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140668. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26469350 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Serum Concentrations in Chronic Post-Stroke Subjects.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2016 Dec;25(12):2968-2974. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2016.08.014. Epub 2016 Sep 1. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2016. PMID: 27593096
-
Decreased Serum Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor May Indicate the Development of Poststroke Depression in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Meta-Analysis.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018 Mar;27(3):709-715. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2017.10.003. Epub 2017 Nov 8. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2018. PMID: 29128330 Review.
-
Effects of phenytoin and lamotrigine treatment on serum BDNF levels in offsprings of epileptic rats.Neuropeptides. 2016 Apr;56:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2015.12.001. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Neuropeptides. 2016. PMID: 26706181 Review.
Cited by
-
A new non-human primate model of photochemically induced cerebral infarction.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e60037. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060037. Epub 2013 Mar 20. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23527298 Free PMC article.
-
Neurotrophin-induced migration and neuronal differentiation of multipotent astrocytic stem cells in vitro.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51706. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051706. Epub 2012 Dec 12. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23251608 Free PMC article.
-
A Chinese Classical Prescription Chaihu Shugan Powder in Treatment of Post-Stroke Depression: An Overview.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Dec 27;59(1):55. doi: 10.3390/medicina59010055. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 36676679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of High Serum Levels of Growth Factors with Good Outcome in Ischemic Stroke: a Multicenter Study.Transl Stroke Res. 2020 Aug;11(4):653-663. doi: 10.1007/s12975-019-00747-2. Epub 2019 Nov 25. Transl Stroke Res. 2020. PMID: 31768951 Free PMC article.
-
Association between brain-derived neurotrophic factor and von Willebrand factor levels in patients with stable coronary artery disease.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2018 Feb 6;18(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s12872-018-0762-z. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2018. PMID: 29409455 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hu Y, Russek SJ. BDNF and the diseases nervous system: a delicate balance between adaptative and pathological process of gene regulation. J Neurochem. 2008;105:1–17. - PubMed
-
- Fujimura H, Altar CA, Chen R, Nakamura T, Nakahashi T, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is stored in human platelets and released by agonist stimulation. Thromb Haemost. 2002;87:728–734. - PubMed
-
- Bayas A, Hummel V, Kallmann BA, Karch C, Toyka KV, et al. Human cerebral endothelial cells are a potential source for bioactive BDNF. Cytokine. 2002;19:55–58. - PubMed
-
- Nakahashi T, Fujimura H, Altar CA, Li J, Kambayashi J, et al. Vascular endothelial cells synthesize and secrete brain-derived neurotrophic factor. FEBS Lett. 2000;470:113–117. - PubMed
-
- Wang H, Ward N, Boswell M, Katz DM. Secretion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor from brain microvascular endothelial cells Eur J Neurosci. 2006;23:1665–1670. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

