A cloud-based simulation architecture for pandemic influenza simulation
- PMID: 22195089
- PMCID: PMC3243184
A cloud-based simulation architecture for pandemic influenza simulation
Abstract
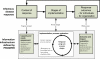
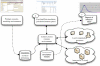
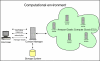
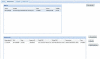
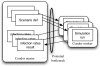
High-fidelity simulations of pandemic outbreaks are resource consuming. Cluster-based solutions have been suggested for executing such complex computations. We present a cloud-based simulation architecture that utilizes computing resources both locally available and dynamically rented online. The approach uses the Condor framework for job distribution and management of the Amazon Elastic Computing Cloud (EC2) as well as local resources. The architecture has a web-based user interface that allows users to monitor and control simulation execution. In a benchmark test, the best cost-adjusted performance was recorded for the EC2 H-CPU Medium instance, while a field trial showed that the job configuration had significant influence on the execution time and that the network capacity of the master node could become a bottleneck. We conclude that it is possible to develop a scalable simulation environment that uses cloud-based solutions, while providing an easy-to-use graphical user interface.
Figures
References
-
- Louz D, Bergmans HE, Loos BP, Hoeben RC. Emergence of viral diseases: mathematical modeling as a tool for infection control, policy and decision making. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2010 Aug;36(3):195–211. - PubMed
-
- Holm E, Timpka T. A discrete time-space geography for epidemiology: from mixing groups to pockets of local order in pandemic simulations. Studies in health technology and informatics. 2007;129:464–468. - PubMed
-
- Eriksson H, Morin M, Jenvald J, Gursky E, Holm E, Timpka T. Ontology based modeling of pandemic simulation scenarios. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2007;129:755–9. - PubMed
-
- Van Kerkhove MD, Asikainen T, Becker NG, Bjorge S, Desenclos JC, dos Santos T, Fraser C, Leung GM, Lipsitch M, Longini IM, Jr, McBryde ES, Roth CE, Shay DK, Smith DJ, Wallinga J, White PJ, Ferguson NM, Riley S. WHO Informal Network for Mathematical Modelling for Pandemic Influenza H1N1 2009 (Working Group on Data Needs). Studies needed to address public health challenges of the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic: insights from modeling. PLoS Med. 2010 Jun 1;7(6):e1000275. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
