The effects of lifestyle modification on symptoms and quality of life in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: a prospective observational study
- PMID: 22195246
- PMCID: PMC3240791
- DOI: 10.5009/gnl.2011.5.4.472
The effects of lifestyle modification on symptoms and quality of life in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: a prospective observational study
Abstract
Background/aims: Although notably common, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) has no specific cure. Lifestyle modification may be as important as medication; however, few studies support the effectiveness of such modifications. We performed this observational study of IBS patients to explore further the role of lifestyle changes in treatment.
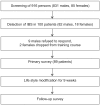
Methods: This study included 831 men who enlisted in 2010 as armed surgeon cadets and 85 women who concurrently entered the Armed Forces Nursing Academy. Of these 916 participants, 89 were diagnosed with IBS using the Rome III criteria. Subjective changes in bowel habits, quality of life, pain, stress, stool frequency and stool consistency were surveyed before and after 9 weeks of army training. We evaluated the lifestyle risk factors that impacted improvement in IBS symptoms by comparing those who responded to lifestyle modification (the responding group) to those who did not respond (the nonresponding group).
Results: More than half of the participants (63%) reported that their symptoms improved after training. The quality of life and levels of pain and stress significantly improved after military training. Initial stress levels before military training and smoking history affected IBS symptom improvement.
Conclusions: Lifestyle modification may be effective in managing IBS patients.
Keywords: Irritable bowel syndrome; Life style; Smoking; Stress.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
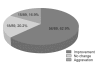

Similar articles
-
Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome, influence of lifestyle factors and bowel habits in Korean college students.Int J Nurs Stud. 2005 Mar;42(3):247-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2004.06.015. Int J Nurs Stud. 2005. PMID: 15708012
-
Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Study of Rifaximin and Lactulose Hydrogen Breath Test in Gulf War Veterans with Irritable Bowel Syndrome.Dig Dis Sci. 2019 Mar;64(3):838-845. doi: 10.1007/s10620-018-5344-5. Epub 2018 Oct 28. Dig Dis Sci. 2019. PMID: 30370492 Clinical Trial.
-
Negative Effects on Psychological Health and Quality of Life of Genuine Irritable Bowel Syndrome-type Symptoms in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Mar;15(3):376-384.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2016.05.012. Epub 2016 May 14. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017. PMID: 27189912
-
Elimination of Fermentable Carbohydrates to Reduce Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Pediatric Patients With Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Narrative Review.Nutr Clin Pract. 2020 Apr;35(2):231-245. doi: 10.1002/ncp.10269. Epub 2019 Apr 1. Nutr Clin Pract. 2020. PMID: 30937981 Review.
-
Modification of Lifestyle to Recover from Post-COVID Symptoms: A Short Review.J Lifestyle Med. 2022 Sep 30;12(3):113-118. doi: 10.15280/jlm.2022.12.3.113. J Lifestyle Med. 2022. PMID: 36628181 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) Haplotype Does Not Influence the Inflammatory Pattern of Duodenal Lymphocytosis Linked to Irritable Bowel Syndrome.Medicina (Kaunas). 2020 Nov 29;56(12):660. doi: 10.3390/medicina56120660. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020. PMID: 33260434 Free PMC article.
-
Complementary and alternative medicines in irritable bowel syndrome: an integrative view.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Jan 14;20(2):346-62. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i2.346. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 24574705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Longer colonic transit time is associated with laxative and drug use, lifestyle factors, and symptoms of constipation.Acta Radiol Open. 2018 Oct 22;7(10):2058460118807232. doi: 10.1177/2058460118807232. eCollection 2018 Sep. Acta Radiol Open. 2018. PMID: 30364803 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between chronotype, social jetlag, and weekday sleep in women with irritable bowel syndrome.Chronobiol Int. 2021 May;38(5):742-752. doi: 10.1080/07420528.2021.1885430. Epub 2021 Feb 22. Chronobiol Int. 2021. PMID: 33612026 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Hypnotherapy and Standard Medical Treatment Alone on Quality of Life in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Randomized Control Trial.J Clin Diagn Res. 2016 May;10(5):OC01-4. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2016/17631.7713. Epub 2016 May 1. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016. PMID: 27437261 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gwee KA, Bak YT, Ghoshal UC, et al. Asian consensus on irritable bowel syndrome. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;25:1189–1205. - PubMed
-
- Han SH, Lee OY, Bae SC, et al. Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome in Korea: population-based survey using the Rome II criteria. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;21:1687–1692. - PubMed
-
- Drossman DA, Whitehead WE, Camilleri M. Irritable bowel syndrome: a technical review for practice guideline development. Gastroenterology. 1997;112:2120–2137. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

