Sodium leak channels in neuronal excitability and rhythmic behaviors
- PMID: 22196327
- PMCID: PMC3247702
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.12.007
Sodium leak channels in neuronal excitability and rhythmic behaviors
Abstract
Extracellular K⁺, Na⁺, and Ca²⁺ ions all influence the resting membrane potential of the neuron. However, the mechanisms by which extracellular Na⁺ and Ca²⁺ regulate basal neuronal excitability are not well understood. Recent findings suggest that NALCN, in association with UNC79 and UNC80, contributes a basal Na⁺ leak conductance in neurons. Mutations in Nalcn, Unc79, or Unc80 lead to severe phenotypes that include neonatal lethality and disruption in rhythmic behaviors. This review discusses the properties of the NALCN complex, its regulation, and its contribution to neuronal function and animal behavior.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
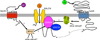
References
-
- Arikkath J, Campbell KP. Auxiliary subunits: essential components of the voltage-gated calcium channel complex. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2003;13:298–307. - PubMed
-
- Baruscotti M, Bucchi A, Viscomi C, Mandelli G, Consalez G, Gnecchi-Rusconi T, Montano N, Casali KR, Micheloni S, Barbuti A, DiFrancesco D. Deep bradycardia and heart block caused by inducible cardiac-specific knockout of the pacemaker channel gene Hcn4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:1705–1710. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

