IKKα activation of NOTCH links tumorigenesis via FOXA2 suppression
- PMID: 22196886
- PMCID: PMC3268914
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.11.018
IKKα activation of NOTCH links tumorigenesis via FOXA2 suppression
Abstract
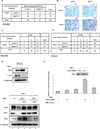
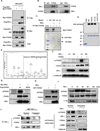
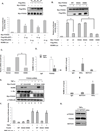
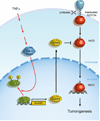
Proinflammatory cytokine TNFα plays critical roles in promoting malignant cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and tumor metastasis in many cancers. However, the mechanism of TNFα-mediated tumor development remains unclear. Here, we show that IKKα, an important downstream kinase of TNFα, interacts with and phosphorylates FOXA2 at S107/S111, thereby suppressing FOXA2 transactivation activity and leading to decreased NUMB expression, and further activates the downstream NOTCH pathway and promotes cell proliferation and tumorigenesis. Moreover, we found that levels of IKKα, pFOXA2 (S107/111), and activated NOTCH1 were significantly higher in hepatocellular carcinoma tumors than in normal liver tissues and that pFOXA2 (S107/111) expression was positively correlated with IKKα and activated NOTCH1 expression in tumor tissues. Therefore, dysregulation of NUMB-mediated suppression of NOTCH1 by TNFα/IKKα-associated FOXA2 inhibition likely contributes to inflammation-mediated cancer pathogenesis. Here, we report a TNFα/IKKα/FOXA2/NUMB/NOTCH1 pathway that is critical for inflammation-mediated tumorigenesis and may provide a target for clinical intervention in human cancer.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Allavena P, Garlanda C, Borrello MG, Sica A, Mantovani A. Pathways connecting inflammation and cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2008;18:3–10. - PubMed
-
- Anest V, Hanson JL, Cogswell PC, Steinbrecher KA, Strahl BD, Baldwin AS. A nucleosomal function for IkappaB kinase-alpha in NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression. Nature. 2003;423:659–663. - PubMed
-
- Balkwill F, Mantovani A. Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet. 2001;357:539–545. - PubMed
-
- Cantarini MC, de la Monte SM, Pang M, Tong M, D'Errico A, Trevisani F, Wands JR. Aspartyl-asparagyl beta hydroxylase over-expression in human hepatoma is linked to activation of insulin-like growth factor and notch signaling mechanisms. Hepatology. 2006;44:446–457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

