Inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway by the curcumin analog, 3,5-Bis(2-pyridinylmethylidene)-4-piperidone (EF31): anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties
- PMID: 22197802
- PMCID: PMC3372981
- DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2011.12.009
Inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway by the curcumin analog, 3,5-Bis(2-pyridinylmethylidene)-4-piperidone (EF31): anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties
Abstract
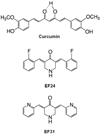
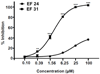
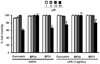
Nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) is a key signaling molecule in the elaboration of the inflammatory response. Data indicate that curcumin, a natural ingredient of the curry spice turmeric, acts as a NF-κB inhibitor and exhibits both anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer properties. Curcumin analogs with enhanced activity on NF-κB and other inflammatory signaling pathways have been developed including the synthetic monoketone compound 3,5-Bis(2-fluorobenzylidene)-4-piperidone (EF24). 3,5-Bis(2-pyridinylmethylidene)-4-piperidone (EF31) is a structurally-related curcumin analog whose potency for NF-κB inhibition has yet to be determined. To examine the activity of EF31 compared to EF24 and curcumin, mouse RAW264.7 macrophages were treated with EF31, EF24, curcumin (1-100 μM) or vehicle (DMSO 1%) for 1h. NF-κB pathway activity was assessed following treatment with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (1 μg/mL). EF31 (IC(50)~5 μM) exhibited significantly more potent inhibition of LPS-induced NF-κB DNA binding compared to both EF24 (IC(50)~35 μM) and curcumin (IC(50) >50 μM). In addition, EF31 exhibited greater inhibition of NF-κB nuclear translocation as well as the induction of downstream inflammatory mediators including pro-inflammatory cytokine mRNA and protein (tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β, and interleukin-6). Regarding the mechanism of these effects on NF-κB, EF31 (IC(50)~1.92 μM) exhibited significantly greater inhibition of IκB kinase β compared to EF24 (IC(50)~131 μM). Finally, EF31 demonstrated potent toxicity in NF-κB-dependent cancer cell lines while having minimal and reversible toxicity in RAW264.7 macrophages. These data indicate that EF31 is a more potent inhibitor of NF-κB activity than either EF24 or curcumin while exhibiting both anti-inflammatory and anticancer activities. Thus, EF31 represents a promising curcumin analog for further therapeutic development.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare, financial or otherwise, regarding findings presented in this manuscript.
Figures








References
-
- Couzin-Frankel J. Inflammation bares a dark side. Science. 2010;330:1621. - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal BB, Shishodia S, Sandur SK, Pandey MK, Sethi G. Inflammation and cancer: how hot is the link? Biochem Pharmacol. 2006;72:1605–1621. - PubMed
-
- Tracy RP. Emerging relationships of inflammation, cardiovascular disease and chronic diseases of aging. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2003;27(Suppl 3):S29–S34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

