Computational design of enhanced learning protocols
- PMID: 22197829
- PMCID: PMC3267874
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.2990
Computational design of enhanced learning protocols
Abstract
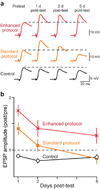
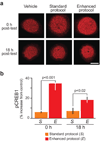
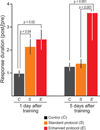
Learning and memory are influenced by the temporal pattern of training stimuli. However, the mechanisms that determine the effectiveness of a particular training protocol are not well understood. We tested the hypothesis that the efficacy of a protocol is determined in part by interactions among biochemical cascades that underlie learning and memory. Previous findings suggest that the protein kinase A (PKA) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) cascades are necessary to induce long-term synaptic facilitation (LTF) in Aplysia, a neuronal correlate of memory. We developed a computational model of the PKA and ERK cascades and used it to identify a training protocol that maximized PKA and ERK interactions. In vitro studies confirmed that the protocol enhanced LTF. Moreover, the protocol enhanced the levels of phosphorylation of the transcription factor CREB1. Behavioral training confirmed that long-term memory also was enhanced by the protocol. These results illustrate the feasibility of using computational models to design training protocols that improve memory.
Figures
Comment in
-
A computational approach enhances learning in Aplysia.Nat Neurosci. 2012 Jan 26;15(2):178-9. doi: 10.1038/nn.3030. Nat Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22281713 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cepeda NJ, Pashler H, Vul E, Wixted JT, Rohrer D. Distributed practice in verbal recall tasks: a review and quantitative synthesis. Psychol. Bull. 2006;132:354–380. - PubMed
-
- Smolen P, Baxter DA, Byrne JH. Frequency selectivity, multistability, and oscillations emerge from models of genetic regulatory systems. Am. J. Physiol. 1998;274:531–542. - PubMed
-
- Byrne JH, et al. Learning and memory: basic mechanisms. In: Byrne JH, Roberts JL, editors. From Molecules to Networks: An Introduction to Cellular and Molecular Neuroscience 2nd edn. Elsevier; 2009. pp. 539–608.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

