Analysis of motoneuron responses to composite synaptic volleys (computer simulation study)
- PMID: 22198533
- PMCID: PMC3282905
- DOI: 10.1007/s00221-011-2987-2
Analysis of motoneuron responses to composite synaptic volleys (computer simulation study)
Abstract
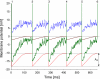
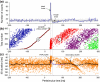
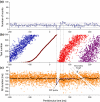
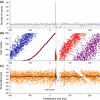
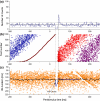
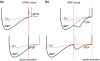
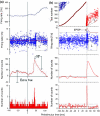
This paper deals with the analysis of changes in motoneuron (MN) firing evoked by repetitively applied stimuli aimed toward extracting information about the underlying synaptic volleys. Spike trains were obtained from computer simulations based on a threshold-crossing model of tonically firing MN, subjected to stimulation producing postsynaptic potentials (PSPs) of various parameters. These trains were analyzed as experimental results, using the output measures that were previously shown to be most effective for this purpose: peristimulus time histogram, raster plot and peristimulus time intervalgram. The analysis started from the effects of single excitatory and inhibitory PSPs (EPSPs and IPSPs). The conclusions drawn from this analysis allowed the explanation of the results of more complex synaptic volleys, i.e., combinations of EPSPs and IPSPs, and the formulation of directions for decoding the results of human neurophysiological experiments in which the responses of tonically firing MNs to nerve stimulation are analyzed.
Figures
References
-
- Ashby P, Zilm D. Characteristics of postsynaptic potentials produced in single human motoneurons by homonymous group 1 volleys. Exp Brain Res. 1982;47:41–48. - PubMed
-
- Ashby P, Zilm D. Relationship between EPSP shape and cross-correlation profile explored by computer simulation for studies on human motoneurons. Exp Brain Res. 1982;47:33–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

