Small-molecule proteostasis regulators for protein conformational diseases
- PMID: 22198733
- PMCID: PMC3262058
- DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.763
Small-molecule proteostasis regulators for protein conformational diseases
Abstract
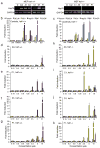
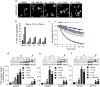
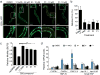
Protein homeostasis (proteostasis) is essential for cellular and organismal health. Stress, aging and the chronic expression of misfolded proteins, however, challenge the proteostasis machinery and the vitality of the cell. Enhanced expression of molecular chaperones, regulated by heat shock transcription factor-1 (HSF-1), has been shown to restore proteostasis in a variety of conformational disease models, suggesting this mechanism as a promising therapeutic approach. We describe the results of a screen comprised of ∼900,000 small molecules that identified new classes of small-molecule proteostasis regulators that induce HSF-1-dependent chaperone expression and restore protein folding in multiple conformational disease models. These beneficial effects to proteome stability are mediated by HSF-1, FOXO, Nrf-2 and the chaperone machinery through mechanisms that are distinct from current known small-molecule activators of the heat shock response. We suggest that modulation of the proteostasis network by proteostasis regulators may be a promising therapeutic approach for the treatment of a variety of protein conformational diseases.
Figures


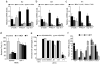
References
-
- Balch WE, Morimoto RI, Dillin A, Kelly JW. Adapting proteostasis for disease intervention. Science. 2008;319:916–9. - PubMed
-
- Powers ET, Morimoto RI, Dillin A, Kelly JW, Balch WE. Biological and chemical approaches to diseases of proteostasis deficiency. Annu Rev Biochem. 2009;78:959–91. - PubMed
-
- Ron D, Walter P. Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:519–29. - PubMed
-
- Haynes CM, Ron D. The mitochondrial UPR - protecting organelle protein homeostasis. J Cell Sci. 2010;123:3849–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS047331/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 MH084512/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 GM038109/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG026647/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- CAPMC/ CIHR/Canada
- R01 GM033301/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM42336/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM038109/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- GM081192/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- AG026647/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL079442/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA070085/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL095524/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG026647/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- GM038109/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- MH084512/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HL 079442/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK785483/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- NS047331/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM042336/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AG000260/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA70085/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

