Regulation of glucose and glycogen metabolism during and after exercise
- PMID: 22199166
- PMCID: PMC3381815
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.224972
Regulation of glucose and glycogen metabolism during and after exercise
Abstract
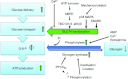
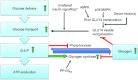
Utilization of carbohydrate in the form of intramuscular glycogen stores and glucose delivered from plasma becomes an increasingly important energy substrate to the working muscle with increasing exercise intensity. This review gives an update on the molecular signals by which glucose transport is increased in the contracting muscle followed by a discussion of glycogen mobilization and synthesis by the action of glycogen phosphorylase and glycogen synthase, respectively. Finally, this review deals with the signalling relaying the well-described increased sensitivity of glucose transport to insulin in the post-exercise period which can result in an overshoot of intramuscular glycogen resynthesis post exercise (glycogen supercompensation).
Figures
References
-
- Antonescu CN, Huang C, Niu W, Liu Z, Eyers PA, Heidenreich KA, Bilan PJ, Klip A. Reduction of insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in L6 myotubes by the protein kinase inhibitor SB203580 is independent of p38MAPK activity. Endocrinology. 2005;146:3773–3781. - PubMed
-
- Aschenbach WG, Suzuki Y, Breeden K, Prats C, Hirshman MF, Dufresne SD, Sakamoto K, Vilardo PG, Steele M, Kim JH, Jing SL, Goodyear LJ, DePaoli-Roach AA. The muscle-specific protein phosphatase PP1G/R(GL)(G(M))is essential for activation of glycogen synthase by exercise. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:39959–39967. - PubMed
-
- Bouskila M, Hunter RW, Ibrahim AF, Delattre L, Peggie M, Diepen vanJA, Voshol PJ, Jensen J, Sakamoto K. Allosteric regulation of glycogen synthase controls glycogen synthesis in muscle. Cell Metab. 2010;12:456–466. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

