Characterization of a highly conserved histone related protein, Ydl156w, and its functional associations using quantitative proteomic analyses
- PMID: 22199229
- PMCID: PMC3322567
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M111.011544
Characterization of a highly conserved histone related protein, Ydl156w, and its functional associations using quantitative proteomic analyses
Abstract
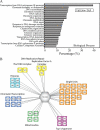
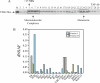
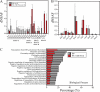
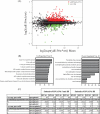
A significant challenge in biology is to functionally annotate novel and uncharacterized proteins. Several approaches are available for deducing the function of proteins in silico based upon sequence homology and physical or genetic interaction, yet this approach is limited to proteins with well-characterized domains, paralogs and/or orthologs in other species, as well as on the availability of suitable large-scale data sets. Here, we present a quantitative proteomics approach extending the protein network of core histones H2A, H2B, H3, and H4 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, among which a novel associated protein, the previously uncharacterized Ydl156w, was identified. In order to predict the role of Ydl156w, we designed and applied integrative bioinformatics, quantitative proteomics and biochemistry approaches aiming to infer its function. Reciprocal analysis of Ydl156w protein interactions demonstrated a strong association with all four histones and also to proteins strongly associated with histones including Rim1, Rfa2 and 3, Yku70, and Yku80. Through a subsequent combination of the focused quantitative proteomics experiments with available large-scale genetic interaction data and Gene Ontology functional associations, we provided sufficient evidence to associate Ydl156w with multiple processes including chromatin remodeling, transcription and DNA repair/replication. To gain deeper insights into the role of Ydl156w in histone biology we investigated the effect of the genetic deletion of ydl156w on H4 associated proteins, which lead to a dramatic decrease in the association of H4 with RNA polymerase III proteins. The implication of a role for Ydl156w in RNA Polymerase III mediated transcription was consequently verified by RNA-Seq experiments. Finally, using these approaches we generated a refined network of Ydl156w-associated proteins.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Recruitment of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Cmr1/Ydl156w to Coding Regions Promotes Transcription Genome Wide.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 5;11(2):e0148897. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148897. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26848854 Free PMC article.
-
Histone release during transcription: NAP1 forms a complex with H2A and H2B and facilitates a topologically dependent release of H3 and H4 from the nucleosome.Biochemistry. 2004 Mar 9;43(9):2359-72. doi: 10.1021/bi035737q. Biochemistry. 2004. PMID: 14992573
-
Transcription-dependent targeting of Hda1C to hyperactive genes mediates H4-specific deacetylation in yeast.Nat Commun. 2019 Sep 19;10(1):4270. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12077-w. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31537788 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast gene CMR1/YDL156W is consistently co-expressed with genes participating in DNA-metabolic processes in a variety of stringent clustering experiments.J R Soc Interface. 2013 Jan 24;10(81):20120990. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2012.0990. Print 2013 Apr 6. J R Soc Interface. 2013. PMID: 23349438 Free PMC article.
-
The multiple faces of Set1.Biochem Cell Biol. 2006 Aug;84(4):536-48. doi: 10.1139/o06-081. Biochem Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16936826 Review.
Cited by
-
A genetic screen for high copy number suppressors of the synthetic lethality between elg1Δ and srs2Δ in yeast.G3 (Bethesda). 2013 May 20;3(5):917-26. doi: 10.1534/g3.113.005561. G3 (Bethesda). 2013. PMID: 23704284 Free PMC article.
-
A noncatalytic function of the topoisomerase II CTD in Aurora B recruitment to inner centromeres during mitosis.J Cell Biol. 2016 Jun 20;213(6):651-64. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201511080. J Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27325791 Free PMC article.
-
The role of WDR76 protein in human diseases.Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2021 Oct 1;21(5):528-534. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2020.5506. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33714259 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Yeast Genome Maintenance by the Multifunctional PIF1 DNA Helicase Family.Genes (Basel). 2020 Feb 20;11(2):224. doi: 10.3390/genes11020224. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32093266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recruitment of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Cmr1/Ydl156w to Coding Regions Promotes Transcription Genome Wide.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 5;11(2):e0148897. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148897. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26848854 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kornberg R. D. (1974) Chromatin structure: a repeating unit of histones and DNA. Science 184, 868–871 - PubMed
-
- Sahasrabuddhe C. G., van Holde K. E. (1974) The effect of trypsin on nuclease-resistant chromatin fragments. J. Biol. Chem. 249, 152–156 - PubMed
-
- Huisinga K. L., Brower-Toland B., Elgin S. C. (2006) The contradictory definitions of heterochromatin: transcription and silencing. Chromosoma 115, 110–122 - PubMed
-
- Murr R. (2010) Interplay between different epigenetic modifications and mechanisms. Adv. Gen. 70, 101–141 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

