7'-[4-(Trifluoro-meth-yl)phen-yl]-5',6',7',7a'-tetra-hydrodispiro-[indan-2,5'-pyrrolo-[1,2-c][1,3]thia-zole-6',2''-indan]-1,3,1''-trione
- PMID: 22199796
- PMCID: PMC3238947
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811047118
7'-[4-(Trifluoro-meth-yl)phen-yl]-5',6',7',7a'-tetra-hydrodispiro-[indan-2,5'-pyrrolo-[1,2-c][1,3]thia-zole-6',2''-indan]-1,3,1''-trione
Abstract
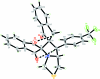
In the title compound, C(29)H(20)F(3)NO(3)S, the thia-zolidine ringadopts a half-chair conformation. The pyrrolidine and two five-membered carbocyclic rings are in envelope conformations with the spiro C atoms at the flaps. The trifluoro-methyl-substituted benzene ring forms dihedral angles of 62.37 (14) and 87.40 (14)° with the benzene rings of the dihydro-1H-indene units. The two benzene rings form a dihedral angle of 36.94 (15)°. The mol-ecular structure is stabilized by intra-molecular C-H⋯O hydrogen bonds, which generate S(6) ring motifs. In the crystal, mol-ecules are linked into inversion dimers by pairs of inter-molecular C-H⋯O hydrogen bonds, generating R(2) (2)(10) ring motifs.
Figures
References
-
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
-
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chamg, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 34, 1555–1573.
-
- Bruker (2009). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Cremer, D. & Pople, J. A. (1975). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97, 1354–1358.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
