[3-({(E)-2-[(4-Fluorophenyl)carbamo-thioyl]hydrazinylidene}methyl)-4-hy-droxy-benzyl]methyl-triphenyl-phos-phonium chloride
- PMID: 22199827
- PMCID: PMC3238978
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536811047945
[3-({(E)-2-[(4-Fluorophenyl)carbamo-thioyl]hydrazinylidene}methyl)-4-hy-droxy-benzyl]methyl-triphenyl-phos-phonium chloride
Abstract
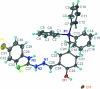
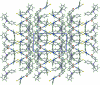
The cation in the title salt, C(33)H(28)FN(3)OPS(+)·Cl(-), is highly twisted with the phospho-nium group occupying a position almost normal to the central hydroxyl-benzene ring [P-C-C-C tosrsion angle = -100.9 (3)°], and with the hydrazone substituent twisted out of the plane [C-C-C-N torsion angle = 13.1 (4)°]. The fluoro-benzene ring is twisted out of the plane of the adjacent thio-urea residue, forming a dihedral angle of 51.69 (10)°. The configuration about the C=N bond [1.281 (4) Å] is E, the O-H and N-H hydrogen atoms are syn, and in the thio-urea residue, the N-H hydrogen atoms are anti, allowing for the formation of an intra-molecular N-H⋯N hydrogen bond. In the crystal, dimeric aggregates mediated by N-H⋯S bonds are formed, which are linked to the Cl(-) anions by O-H⋯Cl hydrogen bonds. The four-component aggregates are linked into a three-dimensional structure by C-H⋯Cl inter-actions.
Figures
References
-
- Agilent (2010). CrysAlis PRO Agilent Technologies, Yarnton, England.
-
- Barbour, L. J. (2001). J. Supramol. Chem. 1, 189–191.
-
- Beraldo, H. & Gambino, D. (2004). Mini Rev. Med. Chem. 4, 31–39. - PubMed
-
- Brandenburg, K. (2006). DIAMOND Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
-
- Kalinowski, D. S., Quach, P. & Richardson, D. R. (2009). Future Med. Chem, 1, 1143–1151. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
