Anti-superoxide and anti-peroxynitrite strategies in pain suppression
- PMID: 22200449
- PMCID: PMC3478755
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.12.008
Anti-superoxide and anti-peroxynitrite strategies in pain suppression
Abstract
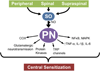
Superoxide (SO, O(2)·(-)) and its reaction product peroxynitrite (PN, ONOO(-)) have been shown to be important in the development of pain of several etiologies. While significant progress has been made in teasing out the relative contribution of SO and PN peripherally, spinally, and supraspinally during the development and maintenance of central sensitization and pain, there is still a considerable void in our understanding. Further research is required in order to develop improved therapeutic strategies for selectively eliminating SO and/or PN. Furthermore, it may be that PN is a more attractive target, in that unlike SO it has no currently known beneficial role. Our group has been at the forefront of research concerning the role of SO and PN in pain, and our current findings have led to the development of two new classes of orally active catalysts which are selective for PN decomposition while sparing SO. This article is part of a Special Issue entitled: Antioxidants and Antioxidant Treatment in Disease.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Melnikova I. Pain market. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010;9:589–590. - PubMed
-
- Foley KM. Misconceptions and controversies regarding the use of opioids in cancer pain. Anticancer Drugs. 1995;6(Suppl 3):4–13. - PubMed
-
- Ossipov MH, Lai J, King T, Vanderah TW, Malan TP, Jr, Hruby VJ, Porreca F. Antinociceptive and nociceptive actions of opioids. J Neurobiol. 2004;61:126–148. - PubMed
-
- Salvemini D, Doyle TM, Cuzzocrea S. Superoxide, peroxynitrite and oxidative/nitrative stress in inflammation. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006;34:965–970. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

