Melatonin: neuritogenesis and neuroprotective effects in crustacean x-organ cells
- PMID: 22200560
- PMCID: PMC3288472
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2011.12.005
Melatonin: neuritogenesis and neuroprotective effects in crustacean x-organ cells
Abstract
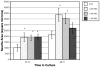
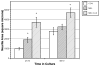
Melatonin has both neuritogenic and neuroprotective effects in mammalian cell lines such as neuroblastoma cells. The mechanisms of action include receptor-coupled processes, direct binding and modulation of calmodulin and protein kinase C, and direct scavenging of free radicals. While melatonin is produced in invertebrates and has influences on their physiology and behavior, little is known about its mechanisms of action. We studied the influence of melatonin on neuritogenesis in well-differentiated, extensively-arborized crustacean x-organ neurosecretory neurons. Melatonin significantly increased neurite area in the first 24h of culture. The more physiological concentrations, 1 nM and 1 pM, increased area at 48 h also, whereas the pharmacological 1 μM concentration appeared to have desensitizing effects by this time. Luzindole, a vertebrate melatonin receptor antagonist, had surprising and significant agonist-like effects in these invertebrate cells. Melatonin receptors have not yet been studied in invertebrates. However, the presence of membrane-bound receptors in this population of crustacean neurons is indicated by this study. Melatonin also has significant neuroprotective effects, reversing the inhibition of neuritogenesis by 200 and 500 μM hydrogen peroxide. Because this is at least in part a direct action not requiring a receptor, melatonin's protection from oxidative stress is not surprisingly phylogenetically-conserved.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Antón-Tay F, Martínez I, Tovar R, Benítez-King G. Modulation of the subcellular distribution of calmodulin by melatonin in MDCK cells. J Pineal Res. 1998a;24:35–42. - PubMed
-
- Antón-Tay F, Ramírez G, Martínez I, Benítez-King G. In vitro stimulation of protein kinase C by melatonin. Neurochem Res. 1998b;23:601–606. - PubMed
-
- Balzer I, Espinola IR, Fuentes-Pardo B. Daily variations of immunoreactive melatonin in the visual system of crayfish. Biol Cell. 1997;89:539–543.
-
- Bellon A, Ortíz-López L, Ramírez-Rodríguez G, Antón-Tay F, Benítez-King G. Melatonin induces neuritogenesis at early stages in N1E-115 cells through actin rearrangements via activation of protein kinase C and Rho-associated kinase. J Pineal Res. 2007;42:214–221. - PubMed
-
- Benítez-King G. PKC activation by melatonin modulates vimentin intermediate filament organization in N1E-115 cells. J Pineal Res. 2000;29:8–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

