Management of hearing aid assembly by urban-dwelling hearing-impaired adults in a developed country: implications for a self-fitting hearing aid
- PMID: 22200734
- PMCID: PMC4040839
- DOI: 10.1177/1084713811431694
Management of hearing aid assembly by urban-dwelling hearing-impaired adults in a developed country: implications for a self-fitting hearing aid
Abstract
A self-fitting hearing aid, designed to be assembled and programmed without audiological or computer support, could bring amplification to millions of people in developing countries, who remain unaided due to the lack of a local, professional, audiological infrastructure. The ability to assemble and insert a hearing aid is fundamental to the successful use of a self-fitting device. In this study, the management of such tasks was investigated. Eighty older, urban-dwelling, hearing-impaired adults in a developed country were asked to follow a set of written, illustrated instructions to assemble two slim-fit behind-the-ear hearing aids. Participants were allowed to access assistance with the task from an accompanying partner. A range of personal and audiometric variables was measured through the use of structured questionnaires and standardized tests of health literacy, cognitive function, and manual dexterity. The results showed that 99% of participants were able to complete the hearing aid assembly task, either on their own or with assistance. Health literacy, or the ability to read and understand health-related text, and gender most strongly influenced participants' ability to complete the assembly task independently and accurately. Higher levels of health literacy were associated with an increased likelihood of independent and successful task completion. Male participants were more likely to complete the task on their own, while female participants were more likely to assemble the device without errors. The results of this study will inform future work regarding development of educational material for the self-fitting hearing aid as well as candidacy for such a device.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

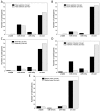
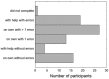
References
-
- Brooks D. N. (1985). Factors relating to the under-use of postaural hearing aids. British Journal of Audiology, 19, 211-217 - PubMed
-
- Buchbinder R., Hall S., Youd J. M. (2006). Functional health literacy of patients with rheumatoid arthritis attending a community-based rheumatology practice. Journal of Rheumatology, 33, 879-886 - PubMed
-
- Dillon H. (2001). Hearing aids. Sydney, Australia: Boomerang Press
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
