Speed, adaptation, and stability of the response to light in cone photoreceptors: the functional role of Ca-dependent modulation of ligand sensitivity in cGMP-gated ion channels
- PMID: 22200947
- PMCID: PMC3250101
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.201110654
Speed, adaptation, and stability of the response to light in cone photoreceptors: the functional role of Ca-dependent modulation of ligand sensitivity in cGMP-gated ion channels
Abstract
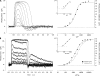
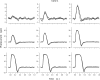
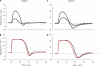
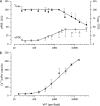
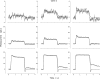
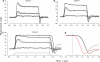
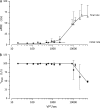
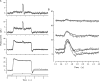
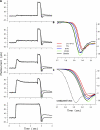
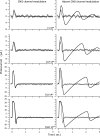
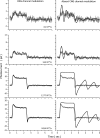
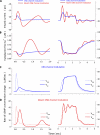
The response of cone photoreceptors to light is stable and reproducible because of the exceptional regulation of the cascade of enzymatic reactions that link visual pigment (VP) excitation to the gating of cyclic GMP (cGMP)-gated ion channels (cyclic nucleotide-gated [CNG]) in the outer segment plasma membrane. Regulation is achieved in part through negative feedback control of some of these reactions by cytoplasmic free Ca(2+). As part of the control process, Ca(2+) regulates the phosphorylation of excited VP, the activity of guanylate cyclase, and the ligand sensitivity of the CNG ion channels. We measured photocurrents elicited by stimuli in the form of flashes, steps, and flashes superimposed on steps in voltage-clamped single bass cones isolated from striped bass retina. We also developed a computational model that comprises all the known molecular events of cone phototransduction, including all Ca-dependent controls. Constrained by available experimental data in bass cones and cone transduction biochemistry, we achieved an excellent match between experimental photocurrents and those simulated by the model. We used the model to explore the physiological role of CNG ion channel modulation. Control of CNG channel activity by both cGMP and Ca(2+) causes the time course of the light-dependent currents to be faster than if only cGMP controlled their activity. Channel modulation also plays a critical role in the regulation of the light sensitivity and light adaptation of the cone photoresponse. In the absence of ion channel modulation, cone photocurrents would be unstable, oscillating during and at the offset of light stimuli.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tuning outer segment Ca2+ homeostasis to phototransduction in rods and cones.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002;514:179-203. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-0121-3_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002. PMID: 12596922 Review.
-
In intact mammalian photoreceptors, Ca2+-dependent modulation of cGMP-gated ion channels is detectable in cones but not in rods.J Gen Physiol. 2004 Jan;123(1):63-75. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200308952. J Gen Physiol. 2004. PMID: 14699078 Free PMC article.
-
CNG-modulin: a novel Ca-dependent modulator of ligand sensitivity in cone photoreceptor cGMP-gated ion channels.J Neurosci. 2012 Feb 29;32(9):3142-53. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5518-11.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22378887 Free PMC article.
-
Time course and Ca(2+) dependence of sensitivity modulation in cyclic GMP-gated currents of intact cone photoreceptors.J Gen Physiol. 2000 Oct;116(4):521-34. doi: 10.1085/jgp.116.4.521. J Gen Physiol. 2000. PMID: 11004202 Free PMC article.
-
Speed, sensitivity, and stability of the light response in rod and cone photoreceptors: facts and models.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2012 Sep;31(5):442-66. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2012.05.002. Epub 2012 May 29. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2012. PMID: 22658984 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of dim-light responses in rod and cone photoreceptors with altered calcium kinetics.J Math Biol. 2023 Oct 12;87(5):69. doi: 10.1007/s00285-023-02005-4. J Math Biol. 2023. PMID: 37823947 Free PMC article.
-
Adhesion GPCR Latrophilin 3 regulates synaptic function of cone photoreceptors in a trans-synaptic manner.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Nov 9;118(45):e2106694118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2106694118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34732574 Free PMC article.
-
A kinetic analysis of mouse rod and cone photoreceptor responses.J Physiol. 2020 Sep;598(17):3747-3763. doi: 10.1113/JP279524. Epub 2020 Jul 14. J Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32557629 Free PMC article.
-
Fractional integral-like processing in retinal cones reduces noise and improves adaptation.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 4;13(10):e0205099. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0205099. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30286168 Free PMC article.
-
EML1 (CNG-modulin) controls light sensitivity in darkness and under continuous illumination in zebrafish retinal cone photoreceptors.J Neurosci. 2013 Nov 6;33(45):17763-76. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2659-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24198367 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baylor D.A. 1987. Photoreceptor signals and vision. Proctor lecture. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 28:34–49 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

