Light inactivation of water transport and protein-protein interactions of aquaporin-Killer Red chimeras
- PMID: 22200949
- PMCID: PMC3250104
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.201110712
Light inactivation of water transport and protein-protein interactions of aquaporin-Killer Red chimeras
Abstract
Aquaporins (AQPs) have a broad range of cellular and organ functions; however, nontoxic inhibitors of AQP water transport are not available. Here, we applied chromophore-assisted light inactivation (CALI) to inhibit the water permeability of AQP1, and of two AQP4 isoforms (M1 and M23), one of which (M23) forms aggregates at the cell plasma membrane. Chimeras containing Killer Red (KR) and AQPs were generated with linkers of different lengths. Osmotic water permeability of cells expressing KR/AQP chimeras was measured from osmotic swelling-induced dilution of cytoplasmic chloride, which was detected using a genetically encoded chloride-sensing fluorescent protein. KR-AQP1 red fluorescence was bleached rapidly (~10% per second) by wide-field epifluorescence microscopy. After KR bleaching, KR-AQP1 water permeability was reduced by up to 80% for the chimera with the shortest linker. Remarkably, CALI-induced reduction in AQP4-KR water permeability was approximately twice as efficient for the aggregate-forming M23 isoform; this suggests intermolecular CALI, which was confirmed by native gel electrophoresis on cells coexpressing M23-AQP4-KR and myc-tagged M23-AQP4. CALI also disrupted the interaction of AQP4 with a neuromyelitis optica autoantibody directed against an extracellular epitope on AQP4. CALI thus permits rapid, spatially targeted and irreversible reduction in AQP water permeability and interactions in live cells. Our data also support the utility of CALI to study protein-protein interactions as well as other membrane transporters and receptors.
Figures



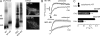
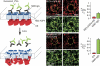

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- HL73856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY013574/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- DK86125/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB000415/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK035124/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK72517/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- EY13574/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- DK35124/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL073856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK072517/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 DK086125/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- EB00415/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK035124/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 EB000415/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

