Smaug1 mRNA-silencing foci respond to NMDA and modulate synapse formation
- PMID: 22201125
- PMCID: PMC3246892
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201108159
Smaug1 mRNA-silencing foci respond to NMDA and modulate synapse formation
Abstract
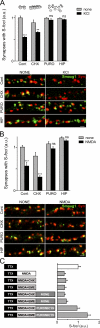
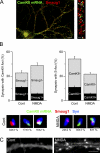
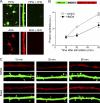
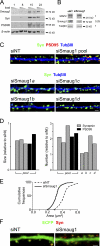
Mammalian Smaug1/Samd4A is a translational repressor. Here we show that Smaug1 forms mRNA-silencing foci located at postsynapses of hippocampal neurons. These structures, which we have named S-foci, are distinct from P-bodies, stress granules, or other neuronal RNA granules hitherto described, and are the first described mRNA-silencing foci specific to neurons. RNA binding was not required for aggregation, which indicates that S-foci formation is not a consequence of mRNA silencing. N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) receptor stimulation provoked a rapid and reversible disassembly of S-foci, transiently releasing transcripts (the CaMKIIα mRNA among others) to allow their translation. Simultaneously, NMDA triggered global translational silencing, which suggests the specific activation of Smaug1-repressed transcripts. Smaug1 is expressed during synaptogenesis, and Smaug1 knockdown affected the number and size of synapses, and also provoked an impaired response to repetitive depolarizing stimuli, as indicated by a reduced induction of Arc/Arg3.1. Our results suggest that S-foci control local translation, specifically responding to NMDA receptor stimulation and affecting synaptic plasticity.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Synaptic control of mRNA translation by reversible assembly of XRN1 bodies.J Cell Sci. 2015 Apr 15;128(8):1542-54. doi: 10.1242/jcs.163295. Epub 2015 Mar 3. J Cell Sci. 2015. PMID: 25736288
-
In neurons, activity-dependent association of dendritically transported mRNA transcripts with the transacting factor CBF-A is mediated by A2RE/RTS elements.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Jun 1;22(11):1864-77. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-11-0904. Epub 2011 Apr 6. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21471000 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA-Binding Protein hnRNP K Mediates the Effect of BDNF on Dendritic mRNA Metabolism and Regulates Synaptic NMDA Receptors in Hippocampal Neurons.eNeuro. 2017 Dec 12;4(6):ENEURO.0268-17.2017. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0268-17.2017. eCollection 2017 Nov-Dec. eNeuro. 2017. PMID: 29255796 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of mRNA untranslated regions on translational efficiency of NMDA receptor subunits.Neurosignals. 2004 Jul-Aug;13(4):194-206. doi: 10.1159/000077526. Neurosignals. 2004. PMID: 15148448 Review.
-
Cataloguing and Selection of mRNAs Localized to Dendrites in Neurons and Regulated by RNA-Binding Proteins in RNA Granules.Biomolecules. 2020 Jan 22;10(2):167. doi: 10.3390/biom10020167. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 31978946 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mitochondrial dysfunction reveals the role of mRNA poly(A) tail regulation in oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy pathogenesis.PLoS Genet. 2015 Mar 27;11(3):e1005092. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005092. eCollection 2015 Mar. PLoS Genet. 2015. PMID: 25816335 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the core exon-junction complex factor eukaryotic initiation factor 4A3 is increased during spatial exploration and striatally-mediated learning.Neuroscience. 2012 Dec 13;226:51-61. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.09.003. Epub 2012 Sep 12. Neuroscience. 2012. PMID: 22982623 Free PMC article.
-
RNA N6-Methyladenosine and the Regulation of RNA Localization and Function in the Brain.Trends Neurosci. 2020 Dec;43(12):1011-1023. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2020.09.005. Epub 2020 Oct 8. Trends Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33041062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smaug/SAMD4A restores translational activity of CUGBP1 and suppresses CUG-induced myopathy.PLoS Genet. 2013 Apr;9(4):e1003445. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003445. Epub 2013 Apr 18. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 23637619 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the RNA-binding protein Smaug by the GPCR Smoothened via the kinase Fused.EMBO Rep. 2020 Jul 3;21(7):e48425. doi: 10.15252/embr.201948425. Epub 2020 May 8. EMBO Rep. 2020. PMID: 32383557 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antar L.N., Afroz R., Dictenberg J.B., Carroll R.C., Bassell G.J. 2004. Metabotropic glutamate receptor activation regulates fragile x mental retardation protein and FMR1 mRNA localization differentially in dendrites and at synapses. J. Neurosci. 24:2648–2655 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0099-04.2004 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

