Astatine-211: production and availability
- PMID: 22201707
- PMCID: PMC3503149
- DOI: 10.2174/1874471011104030177
Astatine-211: production and availability
Abstract
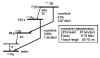
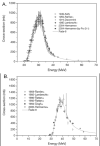
The 7.2-h half life radiohalogen (211)At offers many potential advantages for targeted α-particle therapy; however, its use for this purpose is constrained by its limited availability. Astatine-211 can be produced in reasonable yield from natural bismuth targets via the (209)Bi(α,2n)(211)At nuclear reaction utilizing straightforward methods. There is some debate as to the best incident α-particle energy for maximizing 211At production while minimizing production of (210)At, which is problematic because of its 138.4-day half life α-particle emitting daughter, (210)Po. The intrinsic cost for producing (211)At is reasonably modest and comparable to that of commercially available (123)I. The major impediment to (211)At availability is attributed to the need for a medium energy α-particle beam for its production. On the other hand, there are about 30 cyclotrons in the world that have the beam characteristics required for (211)At production.
Figures
References
-
- Zalutsky MR. Radionuclide therapy. In: Roesch F, editor. Handbook of Nuclear Chemistry: Radiochemistry and Radiopharmaceutical Chemistry in Life Sciences. Volume 4. Kluwer Academic; Dordrecht, Netherlands: 2003. pp. 315–348.
-
- Zalutsky MR, Vaidyanathan G. Astatine-211-labeled radiotherapeutics: an emerging approach to targeted alpha particle therapy. Current Pharm. Design. 2000;6:1433–1455. - PubMed
-
- Milesz S, Norseev YV, Szücs Z, Vasáros L. Characterization of DTPA complexes and conjugated antibodies of astatine. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. Lett. 1989;137:365–372.
-
- Yordanov AT, Deal K, Garmestani K, Kobayashi H, Herring B, Waldman TA, Brechbiel MW. Synthesis and biodistribution study of a new 211At-calix[4]arene complex. J. Label. Compd. Radiopharm. 2000;43:1219–1225.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
