HuR function in disease
- PMID: 22201738
- PMCID: PMC4540328
- DOI: 10.2741/3921
HuR function in disease
Abstract
The cytoplasmic events that control mammalian gene expression, primarily mRNA stability and translation, potently influence the cellular response to internal and external signals. The ubiquitous RNA-binding protein (RBP) HuR is one of the best-studied regulators of cytoplasmic mRNA fate. Through its post-transcriptional influence on specific target mRNAs, HuR can alter the cellular response to proliferative, stress, apoptotic, differentiation, senescence, inflammatory and immune stimuli. In light of its central role in important cellular functions, HuR's role in diseases in which these responses are aberrant is increasingly appreciated. Here, we review the mechanisms that control HuR function, its influence on target mRNAs, and how impairment in HuR-governed gene expression programs impact upon different disease processes. We focus on HuR's well-recognized implication in cancer and chronic inflammation, and discuss emerging studies linking HuR to cardiovascular, neurological, and muscular pathologies. We also discuss the progress, potential, and challenges of targeting HuR therapeutically.
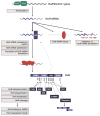
Figures
References
-
- Orphanides G, Reinberg D. A unified theory of gene expression. Cell. 2002;108:439–451. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell P, Tollervey D. mRNA stability in eukaryotes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2000;10:193–198. - PubMed
-
- Keene JD. RNA regulons: coordination of post-transcriptional events. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:533–543. - PubMed
-
- Valencia-Sanchez MA, Liu J, Hannon GJ, Parker R. Control of translation and mRNA degradation by miRNAs and siRNAs. Genes Dev. 2006;20:515–524. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

