Tissue factor pathway inhibitor: structure-function
- PMID: 22201743
- PMCID: PMC3692300
- DOI: 10.2741/3926
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor: structure-function
Abstract
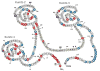
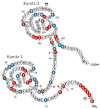
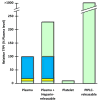
TFPI is a multivalent, Kunitz-type proteinase inhibitor, which, due to alternative mRNA splicing, is transcribed in three isoforms: TFPIalpha, TFPIdelta, and glycosyl phosphatidyl inositol (GPI)-anchored TFPIbeta. The microvascular endothelium is thought to be the principal source of TFPI and TFPIalpha is the predominant isoform expressed in humans. TFPIalpha, apparently attached to the surface of the endothelium in an indirect GPI-anchor-dependent fashion, represents the greatest in vivo reservoir of TFPI. The Kunitz-2 domain of TFPI is responsible for factor Xa inhibition and the Kunitz-1 domain is responsible for factor Xa-dependent inhibition of the factor VIIa/tissue factor catalytic complex. The anticoagulant activity of TFPI in one-stage coagulation assays is due mainly to its inhibition of factor Xa through a process that is enhanced by protein S and dependent upon the Kunitz-3 and carboxyterminal domains of full-length TFPIalpha. Carboxyterminal truncated forms of TFPI as well as TFPIalpha in plasma, however, inhibit factor VIIa/tissue factor in two-stage assay systems. Studies in gene-disrupted mice demonstrate the physiological importance of TFPI.
Figures
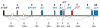
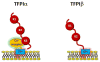
 and O-linked glycosylation sites are denoted at T14, S174 and T175 by
and O-linked glycosylation sites are denoted at T14, S174 and T175 by
 . Partial phosphorylation at Ser2 is also shown
. Partial phosphorylation at Ser2 is also shown
 . The sites of introns in the TFPI gene are labeled with dotted lines and capital letters.
. The sites of introns in the TFPI gene are labeled with dotted lines and capital letters.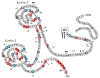

References
-
- Loeb L, Fleisher MS, Tuttle L. The interaction between blood serum and tissue extract in the coagulation of the blood: I. The combined action of serum and tissue extract on fluoride, hirudin, and peptone plasma; the effect of heating on the serum. J Biol Chem. 1922;51:461–483.
-
- Loeb L, Fleisher MS, Tuttle L. The interaction between blood serum and tissue extract in the coagulation of blood: II. A comparison between the effects of the stroma of erythrocytes and of tissue extracts, unheated and heated, on the coagulation of the blood, and on the mechanism of the interaction of these substances with blood serum. J Biol Chem. 1922;51:485–506.
-
- Thomas L. Studies on the intravascular thromboplastin effect of tissue suspensions in mice: II. A factor in normal rabbit serum which inhibits the thromboplastin effect of the sedimentable tissue component. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1947;81:26–42. - PubMed
-
- Schneider CL. The active principle of placental toxin: thromboplastin; its inactivator in blood: antithromboplastin. Am J Physiol. 1947;149:123–129. - PubMed
-
- Mann FD, Hurn M. Inactivation of thromboplastin by serum. Fed Proc. 1949;8:105.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

