Pathologic effects of RNase-L dysregulation in immunity and proliferative control
- PMID: 22202089
- PMCID: PMC3468953
- DOI: 10.2741/s298
Pathologic effects of RNase-L dysregulation in immunity and proliferative control
Abstract
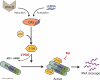
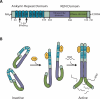
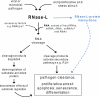
The endoribonuclease RNase-L is the terminal component of an RNA cleavage pathway that mediates antiviral, antiproliferative and immunomodulatory activities. Inactivation or dysregulation of RNase-L is associated with a compromised immune response and increased risk of cancer, accordingly its activity is tightly controlled and requires an allosteric activator, 2',5'-linked oligoadenylates, for enzymatic activity. The biological activities of RNase-L are a result of direct and indirect effects of RNA cleavage and microarray analyses have revealed that RNase-L impacts the gene expression program at multiple levels. The identification of RNase-L-regulated RNAs has provided insights into potential mechanisms by which it exerts antiproliferative, proapoptotic, senescence-inducing and innate immune activities. RNase-L protein interactors have been identified that serve regulatory functions and are implicated as alternate mechanisms of its biologic functions. Thus, while the molecular details are understood for only a subset of RNase-L activities, its regulation by small molecules and critical roles in host defense and as a candidate tumor suppressor make it a promising therapeutic target.
Figures
References
-
- Hovanessian AG. On the discovery of interferon-inducible, double-stranded RNA activated enzymes: the 2'-5'oligoadenylate synthetases and the protein kinase PKR. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2007;18:351–361. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

