Actinium-225 in targeted alpha-particle therapeutic applications
- PMID: 22202153
- PMCID: PMC5565267
- DOI: 10.2174/1874471011104040306
Actinium-225 in targeted alpha-particle therapeutic applications
Abstract
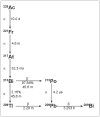
Alpha particle-emitting isotopes are being investigated in radioimmunotherapeutic applications because of their unparalleled cytotoxicity when targeted to cancer and their relative lack of toxicity towards untargeted normal tissue. Actinium- 225 has been developed into potent targeting drug constructs and is in clinical use against acute myelogenous leukemia. The key properties of the alpha particles generated by 225Ac are the following: i) limited range in tissue of a few cell diameters; ii) high linear energy transfer leading to dense radiation damage along each alpha track; iii) a 10 day halflife; and iv) four net alpha particles emitted per decay. Targeting 225Ac-drug constructs have potential in the treatment of cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Milenic DE, Brechbiel MW. Targeting of radio-isotopes for cancer therapy. Cancer Biology & Therapy. 2004;3:361–370. - PubMed
-
- Nikula TK, McDevitt MR, Finn RD, Wu C, Kozak RW, Garmestani K, Brechbiel MW, Curcio MJ, Pippin CG, Tiffany-Jones L, Geerlings MW, Sr, Apostolidis C, Molinet R, Geerlings MW, Jr, Gansow OA, Scheinberg DA. Alpha-emitting bismuth cyclohexylbenzyl DTPA constructs of recombinant humanized anti-CD33 antibodies: pharmacokinetics, bioactivity, toxicity and chemistry. J Nucl Med. 1999;40:166–176. - PubMed
-
- McDevitt MR, Sgouros G, Finn RD, Humm JL, Jurcic JG, Larson SM, Scheinberg DA. Radioimmunotherapy with alpha-emitting nuclides. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine. 1998;25:1341–1351. - PubMed
-
- Friesen C, Glatting G, Koop B, Schwarz K, Morgenstern A, Apostolidis C, Debatin KM, Reske SN. Breaking chemoresistance and radioresistance with [213Bi]anti-CD45 antibodies in leukemia cells. Cancer Research. 2007;67:1950–1958. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
