Lack of efficacy of curcumin on neurodegeneration in the mouse model of Niemann-Pick C1
- PMID: 22202649
- PMCID: PMC3466425
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbb.2011.12.009
Lack of efficacy of curcumin on neurodegeneration in the mouse model of Niemann-Pick C1
Abstract
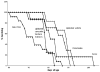
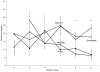
In order to determine the efficacy of curcumin in ameliorating symptoms of neurodegeneration in the mouse model of Niemann-Pick C1, a variety of formulations and dosages of curcumin, one comparable to one previously reported as efficacious, were provided orally to Npc1(-/-)mice. Plasma levels of curcumin, survival, tests of motor performance, and memory (in some cases) were performed. We found variable, but mild, increases in survival (1.5% to 18%). The greatest increased survival occurred with the highest dose (which was unformulated) while the control for the lipidated formulation (containing phosphatidylcholine and stearic acid) had an equivalent impact and other formulations, while not significantly increased, are also not statistically different in effect from the highest dose. We conclude that curcumin is not a highly efficacious treatment for neurodegeneration in Npc1(-/-) mice. Phosphatidylcholine and stearic acid should be studied further.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Defective Cytochrome P450-Catalysed Drug Metabolism in Niemann-Pick Type C Disease.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 28;11(3):e0152007. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152007. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27019000 Free PMC article.
-
Improved neuroprotection using miglustat, curcumin and ibuprofen as a triple combination therapy in Niemann-Pick disease type C1 mice.Neurobiol Dis. 2014 Jul;67:9-17. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2014.03.001. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Neurobiol Dis. 2014. PMID: 24631719
-
Niemann-Pick disease type C1 is a sphingosine storage disease that causes deregulation of lysosomal calcium.Nat Med. 2008 Nov;14(11):1247-55. doi: 10.1038/nm.1876. Epub 2008 Oct 26. Nat Med. 2008. PMID: 18953351
-
Neurological Dysfunction in Early Maturity of a Model for Niemann-Pick C1 Carrier Status.Neurotherapeutics. 2016 Jul;13(3):614-22. doi: 10.1007/s13311-016-0427-5. Neurotherapeutics. 2016. PMID: 26942423 Free PMC article.
-
Niemann-Pick type C disease: molecular mechanisms and potential therapeutic approaches.J Neurochem. 2011 Mar;116(5):789-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2010.06976.x. Epub 2011 Jan 7. J Neurochem. 2011. PMID: 20807315 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Current controversies in Niemann-Pick C1 disease: steroids or gangliosides; neurons or neurons and glia.J Appl Genet. 2013 May;54(2):215-24. doi: 10.1007/s13353-012-0130-0. Epub 2013 Jan 5. J Appl Genet. 2013. PMID: 23292954 Review.
-
Defective Cytochrome P450-Catalysed Drug Metabolism in Niemann-Pick Type C Disease.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 28;11(3):e0152007. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0152007. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27019000 Free PMC article.
-
Rescue of an in vitro neuron phenotype identified in Niemann-Pick disease, type C1 induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neurons by modulating the WNT pathway and calcium signaling.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015 Mar;4(3):230-8. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2014-0127. Epub 2015 Jan 30. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 25637190 Free PMC article.
-
Relative efficacy of nicotinamide treatment of a mouse model of infantile Niemann-Pick C1 disease.J Appl Genet. 2017 Feb;58(1):99-102. doi: 10.1007/s13353-016-0367-0. Epub 2016 Oct 25. J Appl Genet. 2017. PMID: 27783333
-
Diagnostic workup and management of patients with suspected Niemann-Pick type C disease.Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2016 May;9(3):216-29. doi: 10.1177/1756285616635964. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Ther Adv Neurol Disord. 2016. PMID: 27134677 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ader R, Weijnen JAWM, Moleman P. Retention of a passive avoidance response as a function of the intensity and duration of electric shock. Psychon Sci. 1972;26:125–8.
-
- Aggarwal BB, Sundaram C, Malani N, Ichikawa H. Curcumin:the Incian solid gold. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;595:1–75. - PubMed
-
- Baum L, Lam CWK, Cheung SK, Kwok T, Lui V, Tsoh J, et al. Six-Month Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Pilot Clinical Trial of Curcumin in Patients With Alzheimer Disease. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2008;28:110–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources