Lack of efficacy of curcumin on neurodegeneration in the mouse model of Niemann-Pick C1
- PMID: 22202649
- PMCID: PMC3466425
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbb.2011.12.009
Lack of efficacy of curcumin on neurodegeneration in the mouse model of Niemann-Pick C1
Abstract
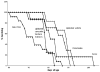
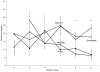
In order to determine the efficacy of curcumin in ameliorating symptoms of neurodegeneration in the mouse model of Niemann-Pick C1, a variety of formulations and dosages of curcumin, one comparable to one previously reported as efficacious, were provided orally to Npc1(-/-)mice. Plasma levels of curcumin, survival, tests of motor performance, and memory (in some cases) were performed. We found variable, but mild, increases in survival (1.5% to 18%). The greatest increased survival occurred with the highest dose (which was unformulated) while the control for the lipidated formulation (containing phosphatidylcholine and stearic acid) had an equivalent impact and other formulations, while not significantly increased, are also not statistically different in effect from the highest dose. We conclude that curcumin is not a highly efficacious treatment for neurodegeneration in Npc1(-/-) mice. Phosphatidylcholine and stearic acid should be studied further.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Ader R, Weijnen JAWM, Moleman P. Retention of a passive avoidance response as a function of the intensity and duration of electric shock. Psychon Sci. 1972;26:125–8.
-
- Aggarwal BB, Sundaram C, Malani N, Ichikawa H. Curcumin:the Incian solid gold. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;595:1–75. - PubMed
-
- Baum L, Lam CWK, Cheung SK, Kwok T, Lui V, Tsoh J, et al. Six-Month Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Pilot Clinical Trial of Curcumin in Patients With Alzheimer Disease. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2008;28:110–3. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources