Automated quantitative Rb-82 3D PET/CT myocardial perfusion imaging: normal limits and correlation with invasive coronary angiography
- PMID: 22203445
- PMCID: PMC3383786
- DOI: 10.1007/s12350-011-9496-3
Automated quantitative Rb-82 3D PET/CT myocardial perfusion imaging: normal limits and correlation with invasive coronary angiography
Abstract
Background: We aimed to characterize normal limits and to determine the diagnostic accuracy for an automated quantification of 3D 82-Rubidium (Rb-82) PET/CT myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI).
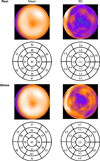
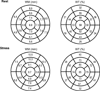
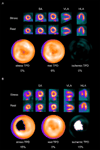
Methods: We studied 125 consecutive patients undergoing Rb-82 PET/CT MPI, including patients with suspected coronary artery disease (CAD) and invasive coronary angiography, and 42 patients with a low likelihood (LLk) of CAD. Normal limits for perfusion and function were derived from LLk patients. QPET software was used to quantify perfusion abnormality at rest and stress expressed as total perfusion deficit (TPD).
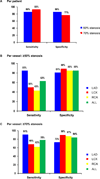
Results: Relative perfusion databases did not differ in any of the 17 segments between males and females. The areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve for detection of CAD were 0.86 for identification of ≥50% and ≥70% stenosis. The sensitivity/specificity was 86%/86% for detecting ≥50% stenosis and 93%/77% for ≥70% stenosis, respectively. In regard to normal limits, mean rest and stress left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) were 67% ± 10% and 75% ± 9%, respectively. Mean transient ischemic dilation ratio was 1.06 ± 0.14 and mean increase in LVEF with stress was 7.4% ± 6.1% (95th percentile of 0%).
Conclusion: Normal limits have been established for 3D Rb-82 PET/CT analysis with QPET software. Fully automated quantification of myocardial perfusion PET data shows high diagnostic accuracy for detecting obstructive CAD.
Conflict of interest statement
Some authors (DB, GG, PJS), receive royalties from the software employed in the study. LM is an employee of Siemens Medical Systems, PET Division. All others disclose no current conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Di Carli MF, Hachamovitch R. New technology for noninvasive evaluation of coronary artery disease. Circulation. 2007;115:1464–1480. - PubMed
-
- Sampson UK, Dorbala S, Limaye A, Kwong R, Di Carli MF. Diagnostic accuracy of rubidium-82 myocardial perfusion imaging with hybrid positron emission tomography/computed tomography in the detection of coronary artery disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007;49:1052–1058. - PubMed
-
- Dorbala S, Vangala D, Sampson U, Limaye A, Kwong R, Di Carli MF. Value of vasodilator left ventricular ejection fraction reserve in evaluating the magnitude of myocardium at risk and the extent of angiographic coronary artery disease: a 82Rb PET/CT study. J Nucl Med. 2007;48:349–358. - PubMed
-
- Stewart RE, Schwaiger M, Molina E, Popma J, Gacioch GM, Kalus M, et al. Comparison of rubidium-82 positron emission tomography and thallium-201 SPECT imaging for detection of coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiol. 1991;67:1303–1310. - PubMed
-
- Go RT, Marwick TH, MacIntyre WJ, Saha GB, Neumann DR, Underwood DA, et al. A prospective comparison of rubidium-82 PET and thallium-201 SPECT myocardial perfusion imaging utilizing a single dipyridamole stress in the diagnosis of coronary artery disease. J Nucl Med. 1990;31:1899–1905. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

