The monoamine oxidase A inhibitor clorgyline is a broad-spectrum inhibitor of fungal ABC and MFS transporter efflux pump activities which reverses the azole resistance of Candida albicans and Candida glabrata clinical isolates
- PMID: 22203607
- PMCID: PMC3294898
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.05706-11
The monoamine oxidase A inhibitor clorgyline is a broad-spectrum inhibitor of fungal ABC and MFS transporter efflux pump activities which reverses the azole resistance of Candida albicans and Candida glabrata clinical isolates
Abstract
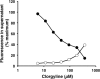
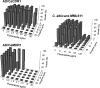
Resistance to the commonly used azole antifungal fluconazole (FLC) can develop due to overexpression of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) and major facilitator superfamily (MFS) plasma membrane transporters. An approach to overcoming this resistance is to identify inhibitors of these efflux pumps. We have developed a pump assay suitable for high-throughput screening (HTS) that uses recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains hyperexpressing individual transporters from the opportunistic fungal pathogen Candida albicans. The recombinant strains possess greater resistance to azoles and other pump substrates than the parental host strain. A flow cytometry-based HTS, which measured increased intracellular retention of the fluorescent pump substrate rhodamine 6G (R6G) within yeast cells, was used to screen the Prestwick Chemical Library (PCL) of 1,200 marketed drugs. Nine compounds were identified as hits, and the monoamine oxidase A inhibitor (MAOI) clorgyline was identified as an inhibitor of two C. albicans ABC efflux pumps, CaCdr1p and CaCdr2p. Secondary in vitro assays confirmed inhibition of pump-mediated efflux by clorgyline. Clorgyline also reversed the FLC resistance of S. cerevisiae strains expressing other individual fungal ABC transporters (Candida glabrata Cdr1p or Candida krusei Abc1p) or the C. albicans MFS transporter Mdr1p. Recombinant strains were also chemosensitized by clorgyline to other azoles (itraconazole and miconazole). Importantly, clorgyline showed synergy with FLC against FLC-resistant C. albicans clinical isolates and a C. glabrata strain and inhibited R6G efflux from a FLC-resistant C. albicans clinical isolate. Clorgyline is a novel broad-spectrum inhibitor of two classes of fungal efflux pumps that acts synergistically with azoles against azole-resistant C. albicans and C. glabrata strains.
Figures


References
-
- Barker KS, Pearson MM, Rogers PD. 2003. Identification of genes differentially expressed in association with reduced azole susceptibility in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 51:1131–1140 - PubMed
-
- Billack B, et al. 2010. Evaluation of the antifungal and plasma membrane H+-ATPase inhibitory action of ebselen and two ebselen analogs in S. cerevisiae cultures. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 25:312–317 - PubMed
-
- Billack B, Santoro M, Lau-Cam C. 2009. Growth inhibitory action of ebselen on fluconazole-resistant Candida albicans: role of the plasma membrane H+-ATPase. Microb. Drug Resist. 15:77–83 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

