A chemokine receptor CXCR2 macromolecular complex regulates neutrophil functions in inflammatory diseases
- PMID: 22203670
- PMCID: PMC3285346
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.315762
A chemokine receptor CXCR2 macromolecular complex regulates neutrophil functions in inflammatory diseases
Abstract
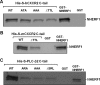
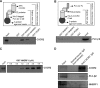
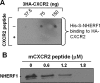
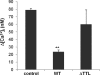
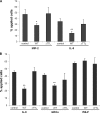
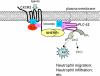
Inflammation plays an important role in a wide range of human diseases such as ischemia-reperfusion injury, arteriosclerosis, cystic fibrosis, inflammatory bowel disease, etc. Neutrophilic accumulation in the inflamed tissues is an essential component of normal host defense against infection, but uncontrolled neutrophilic infiltration can cause progressive damage to the tissue epithelium. The CXC chemokine receptor CXCR2 and its specific ligands have been reported to play critical roles in the pathophysiology of various inflammatory diseases. However, it is unclear how CXCR2 is coupled specifically to its downstream signaling molecules and modulates cellular functions of neutrophils. Here we show that the PDZ scaffold protein NHERF1 couples CXCR2 to its downstream effector phospholipase C (PLC)-β2, forming a macromolecular complex, through a PDZ-based interaction. We assembled a macromolecular complex of CXCR2·NHERF1·PLC-β2 in vitro, and we also detected such a complex in neutrophils by co-immunoprecipitation. We further observed that the CXCR2-containing macromolecular complex is critical for the CXCR2-mediated intracellular calcium mobilization and the resultant migration and infiltration of neutrophils, as disrupting the complex with a cell permeant CXCR2-specific peptide (containing the PDZ motif) inhibited intracellular calcium mobilization, chemotaxis, and transepithelial migration of neutrophils. Taken together, our data demonstrate a critical role of the PDZ-dependent CXCR2 macromolecular signaling complex in regulating neutrophil functions and suggest that targeting the CXCR2 multiprotein complex may represent a novel therapeutic strategy for certain inflammatory diseases.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Structural insights into neutrophilic migration revealed by the crystal structure of the chemokine receptor CXCR2 in complex with the first PDZ domain of NHERF1.PLoS One. 2013 Oct 2;8(10):e76219. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076219. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24098448 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of the NHERF1 PDZ2 domain in complex with the chemokine receptor CXCR2 reveals probable modes of PDZ2 dimerization.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 May 30;448(2):169-74. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.04.085. Epub 2014 Apr 24. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 24768637
-
A critical role of CXCR2 PDZ-mediated interactions in endothelial progenitor cell homing and angiogenesis.Stem Cell Res. 2015 Mar;14(2):133-43. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2014.12.001. Epub 2014 Dec 30. Stem Cell Res. 2015. PMID: 25622052
-
Combined anti CXC receptors 1 and 2 therapy is a promising anti-inflammatory treatment for respiratory diseases by reducing neutrophil migration and activation.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Oct;34:37-45. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2015.08.002. Epub 2015 Aug 10. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 26271598 Review.
-
Interleukin-8: An evolving chemokine.Cytokine. 2022 May;153:155828. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2022.155828. Epub 2022 Mar 2. Cytokine. 2022. PMID: 35247648 Review.
Cited by
-
CXCR2: a target for pancreatic cancer treatment?Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2013 Jun;17(6):667-80. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2013.772137. Epub 2013 Feb 21. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2013. PMID: 23425074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CXCR2 Antagonist RIST4721 Acts as a Potent Chemotaxis Inhibitor of Mature Neutrophils Derived from Ex Vivo-Cultured Mouse Bone Marrow.Biomedicines. 2023 Feb 7;11(2):479. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020479. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36831016 Free PMC article.
-
SMYD2 regulates vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic switching and intimal hyperplasia via interaction with myocardin.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023 Aug 24;80(9):264. doi: 10.1007/s00018-023-04883-9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 37615725 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Association of Chemokine (C-X-C motif) Ligand 1 (CXCL1) with Interstitial Pneumonia with Autoimmune Features (IPAF).Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 13;6:38949. doi: 10.1038/srep38949. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27958346 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dysregulated Chemokine Signaling in Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease: A Potential Therapeutic Target.Curr Drug Targets. 2016;17(13):1535-44. doi: 10.2174/1389450117666151209120516. Curr Drug Targets. 2016. PMID: 26648071 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Geng J. G. (2001) Directional migration of leukocytes. Their pathological roles in inflammation and strategies for development of anti-inflammatory therapies. Cell Res. 11, 85–88 - PubMed
-
- Greene C. M., Carroll T. P., Smith S. G., Taggart C. C., Devaney J., Griffin S., O'Neill S. J., McElvaney N. G. (2005) TLR-induced inflammation in cystic fibrosis and non-cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells. J. Immunol. 174, 1638–1646 - PubMed
-
- Holmes W. E., Lee J., Kuang W. J., Rice G. C., Wood W. I. (1991) Structure and functional expression of a human interleukin-8 receptor. Science 253, 1278–1280 - PubMed
-
- Murphy P. M., Tiffany H. L. (1991) Cloning of complementary DNA encoding a functional human interleukin-8 receptor. Science 253, 1280–1283 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

