Preclinical development of the novel Chk1 inhibitor SCH900776 in combination with DNA-damaging agents and antimetabolites
- PMID: 22203733
- PMCID: PMC3277678
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0406
Preclinical development of the novel Chk1 inhibitor SCH900776 in combination with DNA-damaging agents and antimetabolites
Abstract
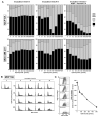
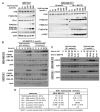
Many anticancer agents damage DNA and arrest cell-cycle progression primarily in S or G(2) phase of the cell cycle. Previous studies with the topoisomerase I inhibitor SN38 have shown the efficacy of the Chk1 inhibitor UCN-01 to overcome this arrest and induce mitotic catastrophe. UCN-01 was limited in clinical trials by unfavorable pharmacokinetics. SCH900776 is a novel and more selective Chk1 inhibitor that potently inhibits Chk1 and abrogates cell-cycle arrest induced by SN38. Like UCN-01, abrogation of SN38-induced arrest enhances the rate of cell death but does not increase overall cell death. In contrast, SCH900776 reduced the growth-inhibitory concentration of hydroxyurea by 20- to 70-fold. A similar magnitude of sensitization was observed with cytarabine. A 5- to 10-fold sensitization occurred with gemcitabine, but no sensitization occurred with cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil, or 6-thioguanine. Sensitization occurred at hydroxyurea concentrations that marginally slowed DNA replication without apparent activation of Chk1, but this led to dependence on Chk1 that increased with time. For example, when added 18 hours after hydroxyurea, SCH900776 induced DNA double-strand breaks consistent with rapid collapse of replication forks. In addition, some cell lines were highly sensitive to SCH900776 alone, and these cells required lower concentrations of SCH900776 to sensitize them to hydroxyurea. We conclude that some tumors may be very sensitive to the combination of SCH900776 and hydroxyurea. Delayed administration of SCH900776 may be more effective than concurrent treatment. SCH900776 is currently in phase I clinical trials, and these results provide the rationale and schedule for future clinical trials.
Figures



References
-
- Sausville EA, Arbuck SG, Messmann R, Headlee D, Bauer KS, Lush RM, et al. Phase I trial of 72-hour continuous infusion UCN-01 in patients with refractory neoplasms. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19:2319–2333. - PubMed
-
- Bunch RT, Eastman A. Enhancement of cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity by 7-hydroxystaurosporine (UCN-01), a new G2-checkpoint inhibitor. Clin Cancer Res. 1996;2:791–797. - PubMed
-
- Kohn EA, Ruth ND, Brown MK, Livingstone M, Eastman A. Abrogation of the S phase DNA damage checkpoint results in S phase progression or premature mitosis depending on the concentration of UCN-01 and the kinetics of Cdc25C activation. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:26553–26564. - PubMed
-
- Wang Q, Fan S, Eastman A, Worland PJ, Sausville EA, O’Connor PM. UCN-01: a potent abrogator of G2 checkpoint function in cancer cells with disrupted p53. J Nat Cancer Inst. 1996;88:956–965. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

