Sodium depletion enhances renal expression of (pro)renin receptor via cyclic GMP-protein kinase G signaling pathway
- PMID: 22203739
- PMCID: PMC3266459
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.186056
Sodium depletion enhances renal expression of (pro)renin receptor via cyclic GMP-protein kinase G signaling pathway
Abstract
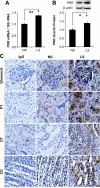
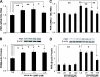
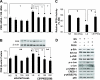
(Pro)renin receptor (PRR) is expressed in renal vasculature, glomeruli, and tubules. The physiological regulation of this receptor is not well established. We hypothesized that sodium depletion increases PRR expression through cGMP- protein kinase G (PKG) signaling pathway. Renal PRR expressions were evaluated in Sprague-Dawley rats on normal sodium or low-sodium diet (LS) and in cultured rat proximal tubular cells and mouse renal inner medullary collecting duct cells exposed to LS concentration. LS augmented PRR expression in renal glomeruli, proximal tubules, distal tubules, and collecting ducts. LS also increased cGMP production and PKG activity. In cells exposed to normal sodium, cGMP analog increased PKG activity and upregulated PRR expression. In cells exposed to LS, blockade of guanylyl cyclase with 1H-(1,2,4)oxadiazolo(4,3-a)quinoxalin-1-one decreased PKG activity and downregulated PRR expression. PKG inhibition decreased phosphatase protein phosphatase 2A activity; suppressed LS-mediated phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase, c-Jun, and nuclear factor-κB p65; and attenuated LS-mediated PRR upregulation. LS also enhanced DNA binding of cAMP response element binding protein 1 to cAMP response elements, nuclear factor-κB p65 to nuclear factor-κB elements, and c-Jun to activator protein 1 elements in PRR promoter in proximal tubular cells. We conclude that sodium depletion upregulates renal PRR expression via the cGMP-PKG signaling pathway by enhancing binding of cAMP response element binding protein 1, nuclear factor-κB p65, and c-Jun to PRR promotor.
Figures

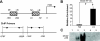

Similar articles
-
In vivo regulation of renal expression of (pro)renin receptor by a low-sodium diet.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012 Dec 15;303(12):F1652-7. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00204.2012. Epub 2012 Oct 17. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012. PMID: 23077099 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of (pro)renin receptor expression by glucose-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase, nuclear factor-kappaB, and activator protein-1 signaling pathways.Endocrinology. 2010 Jul;151(7):3317-25. doi: 10.1210/en.2009-1368. Epub 2010 May 5. Endocrinology. 2010. PMID: 20444941 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II-independent upregulation of cyclooxygenase-2 by activation of the (Pro)renin receptor in rat renal inner medullary cells.Hypertension. 2013 Feb;61(2):443-9. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.112.196303. Epub 2012 Nov 26. Hypertension. 2013. PMID: 23184385 Free PMC article.
-
(Pro)renin receptor contributes to regulation of renal epithelial sodium channel.J Hypertens. 2016 Mar;34(3):486-94; discussion 494. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000000825. J Hypertens. 2016. PMID: 26771338 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble (pro)renin receptor as a novel regulator of renal medullary Na+ reabsorption.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2025 Feb 1;328(2):F239-F247. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00156.2024. Epub 2024 Nov 7. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39508841 Review.
Cited by
-
The critical role of the central nervous system (pro)renin receptor in regulating systemic blood pressure.Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Aug;164:126-34. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.04.006. Epub 2016 Apr 23. Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27113409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Soluble (pro)renin receptor as a potential therapy for diabetes insipidus.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018 Nov 1;315(5):F1416-F1421. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00266.2018. Epub 2018 Jul 18. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30019932 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin II increases the expression of (pro)renin receptor during low-salt conditions.Am J Med Sci. 2014 Nov;348(5):416-22. doi: 10.1097/MAJ.0000000000000335. Am J Med Sci. 2014. PMID: 25250989 Free PMC article.
-
Collecting duct-specific knockout of renin attenuates angiotensin II-induced hypertension.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014 Oct 15;307(8):F931-8. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00367.2014. Epub 2014 Aug 13. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25122048 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of collecting duct renin and (pro)renin receptor in hypertension: mini review.Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2015 Aug;9(4):191-200. doi: 10.1177/1753944715574817. Epub 2015 Mar 16. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis. 2015. PMID: 25780059 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nguyen G, Delarue F, Berrou J, Rondeau E, Sraer JD. Specific receptor binding of renin on human mesangial cells in culture increases plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 antigen. Kidney Int. 1996;50:1897–1903. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

