The application of three-dimensional collagen-scaffolds seeded with myoblasts to repair skeletal muscle defects
- PMID: 22203786
- PMCID: PMC3238809
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/812135
The application of three-dimensional collagen-scaffolds seeded with myoblasts to repair skeletal muscle defects
Abstract
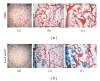
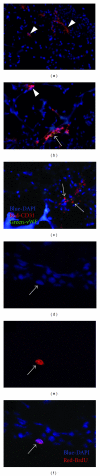
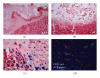
Three-dimensional (3D) engineered tissue constructs are a novel and promising approach to tissue repair and regeneration. 3D tissue constructs have the ability to restore form and function to damaged soft tissue unlike previous methods, such as plastic surgery, which are able to restore only form, leaving the function of the soft tissue often compromised. In this study, we seeded murine myoblasts (C2C12) into a collagen composite scaffold and cultured the scaffold in a roller bottle cell culture system in order to create a 3D tissue graft in vitro. The 3D graft created in vitro was then utilized to investigate muscle tissue repair in vivo. The 3D muscle grafts were implanted into defect sites created in the skeletal muscles in mice. We detected that the scaffolds degraded slowly over time, and muscle healing was improved which was shown by an increased quantity of innervated and vascularized regenerated muscle fibers. Our results suggest that the collagen composite scaffold seeded with myoblasts can create a 3D muscle graft in vitro that can be employed for defect muscle tissue repair in vivo.
Figures




References
-
- Dragas M, Davidovic L, Kostic D, et al. Upper extremity arterial injuries: factors influencing treatment outcome. Injury. 2009;40(8):815–819. - PubMed
-
- Attinger CE, Ducic I, Cooper P, Zelen CM. The role of intrinsic muscle flaps of the foot for bone coverage in foot and ankle defects in diabetic and nondiabetic patients. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2002;110(4):1047–1054. - PubMed
-
- Singh AK, Gudehithlu KP, Patri S, et al. Impaired integration of endothelial progenitor cells in capillaries of diabetic wounds is reversible with vascular endothelial growth factor infusion. Translational Research. 2007;149(5):282–291. - PubMed
-
- Al-Qattan MM. Severe, traumatic soft-tissue loss in the antecubital fossa and proximal forearm associated with radial and/or median nerve palsy: nerve recovery after coverage with a pedicled latissimus dorsi muscle flap. Annals of Plastic Surgery. 2001;46(2):125–129. - PubMed
-
- Takeuchi A, Tsuchiya H, Shirai T, Hayashi K, Nishida H, Tomita K. Occlusive dressing for large soft tissue defects following soft tissue tumor excision. Journal of Orthopaedic Science. 2009;14(4):385–390. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

