Diabetic nephropathy amelioration by a low-dose sitagliptin in an animal model of type 2 diabetes (Zucker diabetic fatty rat)
- PMID: 22203828
- PMCID: PMC3235777
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/162092
Diabetic nephropathy amelioration by a low-dose sitagliptin in an animal model of type 2 diabetes (Zucker diabetic fatty rat)
Abstract
This study was performed to assess the effect of chronic low-dose sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor, on metabolic profile and on renal lesions aggravation in a rat model of type-2 diabetic nephropathy, the Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) rat. Diabetic and obese ZDF (fa/fa) rats and their controls ZDF (+/+) were treated for 6 weeks with vehicle (control) or sitagliptin (10 mg/kg/bw). Blood/serum glucose, HbA1c, insulin, Total-c, TGs, urea, and creatinine were assessed, as well as kidney glomerular and tubulointerstitial lesions (interstitial fibrosis/tubular atrophy), using a semiquantitative rating from 0 (absent/normal) to 3 (severe and extensive damage). Vascular lesions were scored from 0-2. Sitagliptin in the diabetic rats promoted an amelioration of glycemia, HbA1c, Total-c, and TGs, accompanied by a partial prevention of insulinopenia. Furthermore, together with urea increment prevention, renal lesions were ameliorated in the diabetic rats, including glomerular, tubulointerstitial, and vascular lesions, accompanied by reduced lipid peroxidation. In conclusion, chronic low-dose sitagliptin treatment was able to ameliorate diabetic nephropathy, which might represent a key step forward in the management of T2DM and this serious complication.
Copyright © 2011 Cristina Mega et al.
Figures

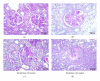
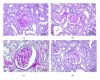

References
-
- Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(5):1047–1053. - PubMed
-
- Gray SP, Cooper ME. Diabetic nephropathy in 2010: alleviating the burden of diabetic nephropathy. Nature Reviews Nephrology. 2011;7(2):71–73. - PubMed
-
- Marchant K. Diabetes and chronic kidney disease: a complex combination. British Journal of Nursing. 2008;17(6):356–361. - PubMed
-
- Crawford MH. Diabetes, the kidney, and cardiovascular risk. Foreword. Cardiology Clinics. 2010;28(3):p. 9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
