Iron inhibits respiratory burst of peritoneal phagocytes in vitro
- PMID: 22203913
- PMCID: PMC3236377
- DOI: 10.5402/2011/605436
Iron inhibits respiratory burst of peritoneal phagocytes in vitro
Abstract
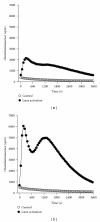
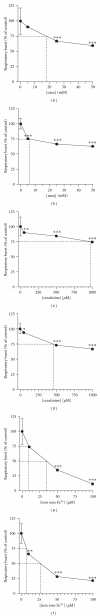
Objective. This study examines the effects of iron ions Fe(3+) on the respiratory burst of phagocytes isolated from peritoneal effluents of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) patients, as an in vitro model of iron overload in end-stage renal disease (ESRD). Material and Methods. Respiratory burst of peritoneal phagocytes was measured by chemiluminescence method. Results. At the highest used concentration of iron ions Fe(3+) (100 μM), free radicals production by peritoneal phagocytes was reduced by 90% compared to control. Conclusions. Iron overload may increase the risk of infectious complications in ESRD patients.
Figures
References
-
- Valderrâbano F. Erythropoietin in chronic renal failure. Kidney International. 1996;50(4):1373–1391. - PubMed
-
- Macdougall IC, Chandler G, Elston O, Harchowal J. Beneficial effects of adopting an aggressive intravenous iron policy in a hemodialysis unit. American Journal of Kidney Diseases. 1999;34(4, supplement 2):S40–S46. - PubMed
-
- Eschbach J, DeOreo P, Adamson J, et al. NKF-DOQI clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of anemia of chronic renal failure. American Journal of Kidney Diseases. 1997;30(supplement 3):S192–S240. - PubMed
-
- Anderson GJ. Mechanisms of iron loading and toxicity. American Journal of Hematology. 2007;82(12):1128–1131. - PubMed
-
- Walker EM, Jr., Walker SM. Eeffects of iron overload on the immune system. Annals of Clinical and Laboratory Science. 2000;30(4):354–365. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
