Single-cell proteomic chip for profiling intracellular signaling pathways in single tumor cells
- PMID: 22203961
- PMCID: PMC3258586
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1110865109
Single-cell proteomic chip for profiling intracellular signaling pathways in single tumor cells
Abstract
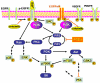
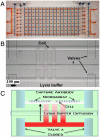
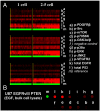
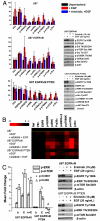
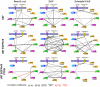
We describe a microchip designed to quantify the levels of a dozen cytoplasmic and membrane proteins from single cells. We use the platform to assess protein-protein interactions associated with the EGF-receptor-mediated PI3K signaling pathway. Single-cell sensitivity is achieved by isolating a defined number of cells (n = 0-5) in 2 nL volume chambers, each of which is patterned with two copies of a miniature antibody array. The cells are lysed on-chip, and the levels of released proteins are assayed using the antibody arrays. We investigate three isogenic cell lines representing the cancer glioblastoma multiforme, at the basal level, under EGF stimulation, and under erlotinib inhibition plus EGF stimulation. The measured protein abundances are consistent with previous work, and single-cell analysis uniquely reveals single-cell heterogeneity, and different types and strengths of protein-protein interactions. This platform helps provide a comprehensive picture of altered signal transduction networks in tumor cells and provides insight into the effect of targeted therapies on protein signaling networks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Reynoso D, Trent JC. Neoadjuvant and adjuvant imatinib treatment in gastrointestinal stromal tumor: Current status and recent developments. Curr Opin Oncol. 2010;22:330–335. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

