Eph-dependent cell-cell adhesion and segregation in development and cancer
- PMID: 22204021
- PMCID: PMC11114713
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-011-0900-6
Eph-dependent cell-cell adhesion and segregation in development and cancer
Abstract
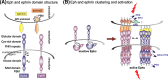
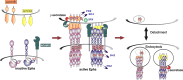
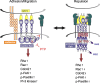
Numerous studies attest to essential roles for Eph receptors and their ephrin ligands in controlling cell positioning and tissue patterning during normal and oncogenic development. These studies suggest multiple, sometimes contradictory, functions of Eph-ephrin signalling, which under different conditions can promote either spreading and cell-cell adhesion or cytoskeletal collapse, cell rounding, de-adhesion and cell-cell segregation. A principle determinant of the balance between these two opposing responses is the degree of receptor/ligand clustering and activation. This equilibrium is likely altered in cancers and modulated by somatic mutations of key Eph family members that have emerged as candidate cancer markers in recent profiling studies. In addition, cross-talk amongst Ephs and with other signalling pathways significantly modulates cell-cell adhesion, both between and within Eph- and ephrin-expressing cell populations. This review summarises our current understanding of how Eph receptors control cell adhesion and morphology, and presents examples demonstrating the importance of these events in normal development and cancer.
Figures
References
-
- Lackmann M, Boyd AW (2008) Eph, a protein family coming of age: more confusion, insight, or complexity? Sci Signal 1: re2 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

